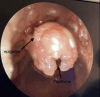
Emergency Debulking of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: An Anesthesia Challenge
- PMID: 39723302
- PMCID: PMC11669302
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.74404
Emergency Debulking of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: An Anesthesia Challenge
Abstract
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (RRP) is a rare condition involving the recurrent growth of benign papillomas in the respiratory tract caused exclusively by human papillomavirus (HPV). We present the case of a five-year-old child who arrived at the emergency department with severe respiratory distress, hoarseness, and biphasic stridor. The patient required urgent transfer to the operating room for the emergency debridement of papillomas. Managing emergency pediatric airway obstruction poses significant anesthetic challenges and requires specialized skills and dedicated pediatric tertiary care facilities.
Keywords: airway; anaesthesia; distress; emergency; hoarsness; papilloma.
Copyright © 2024, Padvi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Presenting Symptom as a Predictor of Clinical course in Juvenile Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis.Laryngoscope. 2021 Jul;131(7):1670-1675. doi: 10.1002/lary.29327. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Laryngoscope. 2021. PMID: 33331659
-
Clinical Activity of Nivolumab for Human Papilloma Virus-Related Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis.Oncologist. 2019 Jun;24(6):829-835. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0505. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30842242 Free PMC article.
-
Novel treatments for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2002 Aug;11(8):1139-48. doi: 10.1517/13543784.11.8.1139. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12150707 Review.
-
Anesthetic management for laser excision of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis in a third trimester parturient.J Clin Anesth. 2005 Dec;17(8):610-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2005.01.011. J Clin Anesth. 2005. PMID: 16427531
-
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A state-of-the-art review.Respir Med. 2017 May;126:116-121. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2017.03.030. Epub 2017 Apr 1. Respir Med. 2017. PMID: 28427542 Review.
References
-
- Overview of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Wiatrak BJ. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;11:433–441. - PubMed
-
- Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: a state-of-the-art review. Fortes HR, von Ranke FM, Escuissato DL, et al. Respir Med. 2017;126:116–121. - PubMed
-
- Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: a review. Derkay CS, Wiatrak B. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLG.0b013e31816a7135. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:1236–1247. - PubMed
-
- Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis with complete response to systemic bevacizumab therapy. Gorelik D, Frantz A, Dome JS, Reilly BK. Ear Nose Throat J. 2024;103:100–101. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources