Probiotic interventions in peritoneal dialysis: A review of underlying mechanisms and therapeutic potentials
- PMID: 39723354
- PMCID: PMC11572655
- DOI: 10.5527/wjn.v13.i4.98719
Probiotic interventions in peritoneal dialysis: A review of underlying mechanisms and therapeutic potentials
Abstract
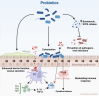
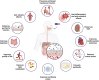
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a commonly used modality for kidney replacement therapy for patients with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). PD offers many benefits, including home-based care, greater flexibility, and preservation of residual kidney function compared to in-center hemodialysis. Nonetheless, patients undergoing PD often face significant challenges, including systemic inflammation, PD-related peritonitis, metabolic disorders, and cardiovascular issues that can negatively affect their quality of life and treatment outcomes. Recent studies have demonstrated the crucial role of the gut microbiome in overall health and treatment results, supporting the hypothesis that probiotics may bring potential benefits to the general population of ESKD patients. However, specific data on probiotic use in PD patients are limited. This opinion review aims to summarize the current knowledge on the relationship between PD and the gut microbiome and offers a novel perspective by specifically exploring how probiotic interventions could improve the outcomes of PD treatment. The review also outlines some clinical data supporting the effectiveness of probiotics in patients undergoing PD and considers the difficulties and restrictions in their application. Based on the current knowledge gaps, this study seeks to explore future research directions and their implications for clinical practice.
Keywords: Effectiveness; Gut; Inflammation; Microbiota; Peritoneal dialysis; Probiotics; Treatment.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Dr. Stepanova has nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Potential Benefits and Controversies of Probiotics Use in Patients at Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 29;14(19):4044. doi: 10.3390/nu14194044. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knowledge about peritoneal dialysis among patients with end-stage kidney disease on hemodialysis: a cross-sectional study.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2411019. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2411019. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39376132 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota in Patients Receiving Dialysis: A Review.Pathogens. 2024 Sep 15;13(9):801. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13090801. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39338992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peritoneal Microbiome in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients and the Impact of Peritoneal Dialysis Therapy.Microorganisms. 2020 Jan 25;8(2):173. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8020173. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 31991821 Free PMC article.
-
Dyslipidemia in Peritoneal Dialysis: Implications for Peritoneal Membrane Function and Patient Outcomes.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 17;12(10):2377. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102377. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457689 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tryptophan metabolism as a target in gut microbiota, ageing and kidney disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jun 23;21(10):4374-4387. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.115359. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40765836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fecal microbiota transplantation is a promising therapy for kidney diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 9;12:1628722. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1628722. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40703302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiome remodeling in chronic kidney disease: implications of kidney replacement therapies and therapeutic interventions.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 15;12:1620247. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1620247. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40735439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The alternations of gut microbiota in diabetic kidney disease: insights from a triple comparative cohort.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 27;15:1606700. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1606700. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40654567 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic nutritional index as a predictor of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in chronic kidney disease: a population-based analysis of NHANES data (1999-2018).Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 6;12:1589173. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1589173. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40547920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Briggs V, Davies S, Wilkie M. International Variations in Peritoneal Dialysis Utilization and Implications for Practice. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;74:101–110. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

