Influence of interoception and body movement on the rubber hand illusion
- PMID: 39723393
- PMCID: PMC11669270
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1458726
Influence of interoception and body movement on the rubber hand illusion
Abstract
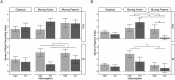
Rubber hand illusion (RHI) refers to the illusory sense of body ownership of a fake hand, which is induced by synchronous visuotactile stimulation to the real and fake hands. A negative correlation was reported between the cardiac interoception and the strength of RHI, but the subsequent studies have been unsuccessful in replicating it. On the other hand, voluntary action is suggested to link interoception and the sense of body ownership in different situations. If so, moving RHI, induced by the active or the passive finger tapping while observing a fake hand, might reveal the relationship more clearly. The measurement of interoception has been another issue. We, therefore, examined the relationship between the moving RHI and two measures of interoception: interoceptive accuracy (IAcc) measured by the conventional heartbeat counting task and interoceptive sensibility (IS) measured using a questionnaire. For the classical visuotactile RHI, our results supported the lack of association between the interoception measures and RHI. For the moving RHI, a stronger sense of body ownership was induced for participants with higher IS regardless of active or passive movement, and a stronger sense of agency was caused by active than passive movement only for those with lower IAcc. These results reveal the dynamic links between the interoception and the bodily senses. The results also suggest that multiple dimensions of interoception affect the bodily senses differently.
Keywords: body movement; interoception; rubber hand illusion; sense of agency; sense of body ownership.
Copyright © 2024 Kaneno, Pasqualotto and Ashida.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interoceptive ingredients of body ownership: Affective touch and cardiac awareness in the rubber hand illusion.Cortex. 2018 Jul;104:180-192. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2017.04.018. Epub 2017 May 1. Cortex. 2018. PMID: 28532579
-
The tangled threads: Unveiling the interplay between the sense of body ownership and the sense of agency in impacting the bodily-self representation in eating disorders.Cortex. 2025 Apr;185:270-285. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2025.02.011. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Cortex. 2025. PMID: 40107169
-
The Moving Rubber Hand Illusion Reveals that Explicit Sense of Agency for Tapping Movements Is Preserved in Functional Movement Disorders.Front Hum Neurosci. 2017 Jun 6;11:291. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00291. eCollection 2017. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28634447 Free PMC article.
-
Mu Rhythm Desynchronization while Observing Rubber Hand Movement in the Mirror: The Interaction of Body Representation with Visuo-Tactile Stimulation.Brain Sci. 2023 Jun 19;13(6):969. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13060969. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37371446 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbances in body ownership in schizophrenia: evidence from the rubber hand illusion and case study of a spontaneous out-of-body experience.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e27089. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027089. Epub 2011 Oct 31. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22073126 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
It Is Movement All the Way Down: Broken Rhythms and Embodied Selfhood in Depersonalization.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Aug 12;15(8):1090. doi: 10.3390/bs15081090. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cabrera A., Kolacz J., Pailhez G., Bulbena-Cabre A., Bulbena A., Porges S. W. (2018). Assessing body awareness and autonomic reactivity: factor structure and psychometric properties of the body perception questionnaire-short form (BPQ-SF). Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 27:e1596. doi: 10.1002/mpr.1596, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

