Artificial intelligence-assisted echocardiographic monitoring in pediatric patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- PMID: 39723412
- PMCID: PMC11669191
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1418741
Artificial intelligence-assisted echocardiographic monitoring in pediatric patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Abstract
Background: Percutaneous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is administered to pediatric patients with cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. The traditional method uses focal echocardiography to complete the left ventricular measurement. However, echocardiographic determination of the ejection fraction (EF) by manual tracing of the endocardial borders is time consuming and operator dependent. The standard visual assessment is also an inherently subjective procedure. Artificial intelligence (AI) based machine learning-enabled image analysis might provide rapid, reproducible measurements of left ventricular volumes and EF for ECMO patients.
Objectives: This study aims to evaluate the applicability of AI for monitoring cardiac function based on Echocardiography in patients with ECMO.
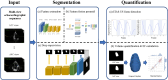
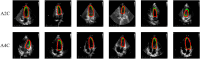
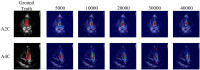
Materials and methods: We conducted a retrospective study involving 29 hospitalized patients who received ECMO support between January 2017 and December 2021. Echocardiogram was performed for patients with ECMO, including at pre-ECMO, during cannulation, during ECMO support, during the ECMO wean, and a follow up within 3 months after weaning. EF assessment of all patients was independently evaluated by junior physicians (junior-EF) and experts (expert-EF) using Simpson's biplane method of manual tracing. Additionally, raw data images of apical 2-chamber and 4-chamber views were utilized for EF assessment via a Pediatric ECMO Quantification machine learning-enabled AI (automated-EF).
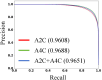
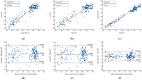
Results: There was no statistically significant difference between the automated-EF and expert-EF for all groups (P > 0.05). However, the differences between junior-EF and automated-EF and expert-EF were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Inter-group correlation coefficients (ICC) indicated higher agreement between automated-EF and expert manual tracking (ICC: 0.983, 95% CI: 0.977∼0.987) compared to junior assessments (ICC: 0.932, 95% CI: 0.913∼0.946). Bland-Altman analysis showed good agreements among the automated-EF and the expert-EF and junior-EF assessments. There was no significant intra-observer variability for experts' manual tracking or automated measurements.
Conclusions: Automated EF measurements are feasible for pediatric ECMO echocardiography. AI-automated analysis of echocardiography for quantifying left ventricular function in critically ill children has good consistency and reproducibility with that of clinical experts. The automated echocardiographic EF method is reliable for the quantitative evaluation of different heart rates. It can fully support the course of ECMO treatment, and it can help improve the accuracy of quantitative evaluation.
Keywords: ECMO; artificial intelligence; critical monitoring; echocardiography; left ventricular function; pediatrics.
© 2024 Chen, Wu, Zhang, Gao, Chen, Zhang, Lin, Tang, Yu, Fan, Zhang and Xia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fully Automated Versus Standard Tracking of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction and Longitudinal Strain: The FAST-EFs Multicenter Study.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015 Sep 29;66(13):1456-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.07.052. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26403342
-
Automated Echocardiographic Quantification of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Without Volume Measurements Using a Machine Learning Algorithm Mimicking a Human Expert.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Sep;12(9):e009303. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009303. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31522550 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of left ventricular ejection fraction and cardiac output using a novel semi-automated echocardiographic method: a prospective observational study in coronary artery bypass patients.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Feb 28;23(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02025-z. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 36855077 Free PMC article.
-
Parameters associated with successful weaning of veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: a systematic review.Crit Care. 2022 Dec 5;26(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04249-w. Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 36471408 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Cardiac Indications in Adults: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020 Mar 6;20(8):1-121. eCollection 2020. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020. PMID: 32284771 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

