Exploring the effect and mechanism of action of Jinlida granules (JLD) in the treatment of diabetes-associated cognitive impairment based on network pharmacology with experimental validation
- PMID: 39723533
- PMCID: PMC11703463
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2445181
Exploring the effect and mechanism of action of Jinlida granules (JLD) in the treatment of diabetes-associated cognitive impairment based on network pharmacology with experimental validation
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the effect and the probable mechanisms of JLD in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) - associated cognitive impairment (TDACI).
Methods: The effect of JLD in combating TDACI was assessed in T2DM model mice by conducting Morris water maze (MWM) behaviour testing. Active components and their putative targets, as well as TDACI-related targets, were collected from public databases. Protein-protein interactions (PPIs), Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses and molecular docking were then utilized to explore potential molecular network mechanisms. Finally, the main targets were verified in animal model experiments.
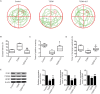
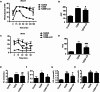
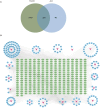
Results: MWM test showed that JLD improved aspects of behaviour in T2DM model mice. JLD improved glucose intolerance, tissue insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism and enhanced synapse-associated protein expression in hippocampus tissue. Network pharmacology revealed 185 active components, 337 targets of JLD, and 7998 TDACI related targets were obtained . PPI network analyses revealed 39 core targets. GO and KEGG analyses suggested that JLD might improve TDACI by regulating gene expression, apoptotic processes and inflammatory responses mainly via PI3K-AKT and AGE-RAGE signaling pathways. Molecular docking revealed strong binding of the main components to core targets. JLD reduced hippocampus tissue expression of the inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL6), core targets of treatment of TDACI.
Conclusions: The findings suggested that JLD has the potential to improve TDACI through multiple components, multiple targets and multiple pathways. JLD may be a promising treatment for diabetic cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Jinlida granule; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; cognitive impairment; inflammation; network pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures



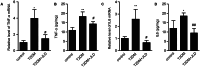
References
-
- Pal K, Mukadam N, Petersen I, et al. Mild cognitive impairment and progression to dementia in people with diabetes, prediabetes and metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2018;53(11):1149–1160. doi: 10.1007/s00127-018-1581-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
