Ultrastructural imaging biomarkers in diabetic macular edema: A major review
- PMID: 39723865
- PMCID: PMC11834929
- DOI: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_878_24
Ultrastructural imaging biomarkers in diabetic macular edema: A major review
Abstract
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a vision-threatening complication of diabetic retinopathy and causes significant morbidity in patients. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents are the mainstay of treatment for DME, with steroid implants being used for the treatment of anti-VEGF resistant eyes. Over the years, several classification systems have been devised to describe the patterns of DME using optical coherence tomography (OCT). With the advent of effective treatments, it has become imperative that imaging cues are not merely used for classifying the disease but also as biomarkers for prognostication of disease activity and treatment response. In this aspect, newer imaging findings such as hyperreflective dots, photoreceptor integrity, and disorganization of retinal inner layers have been characterized in detail by several authors. Macular perfusion analysis using OCT angiography is the latest in the armamentarium for imaging DME. In this narrative review, we have summarized all relevant literature related to the ultrastructural imaging-based biomarkers of DME and their correlation to treatment.
Copyright © 2024 Indian Journal of Ophthalmology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
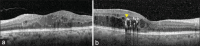
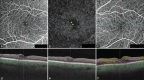
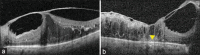
Figures





References
-
- Aiello LP, Gardner TW, King GL, Blankenship G, Cavallerano JD, Ferris FL, et al. Diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:143–56. - PubMed
-
- Techniques for scatter and local photocoagulation treatment of diabetic retinopathy: Early treatment diabetic retinopathy study report no. 3. The early treatment diabetic retinopathy study research group. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1987;27:254–64. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL, Klein RE, Lee PP, Agardh CD, Davis M, et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:1677–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

