Sub-toxic cisplatin concentrations induce extensive chromosomal, nuclear and nucleolar abnormalities associated with high malignancy before acquired resistance develops: Implications for clinical caution
- PMID: 39724069
- PMCID: PMC11670937
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311976
Sub-toxic cisplatin concentrations induce extensive chromosomal, nuclear and nucleolar abnormalities associated with high malignancy before acquired resistance develops: Implications for clinical caution
Abstract
Aim: This study investigates the impact of sub-toxic cisplatin levels on nuclear and nucleolar abnormalities and chromosome instability in HeLa cells since our current knowledge of cisplatin effects on these parameters is based on studies with high concentrations of cisplatin.
Materials and methods: HeLa cells were exposed to gradually increasing sub-toxic doses of cisplatin (0.01 to 0.2 μg/ml). Cells treated with 0.1 and 0.2 μg/ml, termed HeLaC0.1 and HeLaC0.2, were not cisplatin-resistant, only exhibiting a slightly reduced viability, and were termed "cisplatin-sensitized cells." Giemsa and silver staining were used to detect nuclear and nucleolar abnormalities and chromosomal alterations.
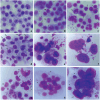
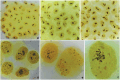
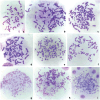
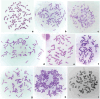
Results: Notable abnormalities were observed in HeLaC0.1 and HeLaC0.2 cells after treatment with sub-toxic concentrations of cisplatin: nuclei showed abnormal shapes, blebs, micronuclei, fragmentation, pulverization, and multinucleation; nucleoli exhibited irregular shapes and increased numbers; anaphase cells showed more nucleolar organizing regions. Abnormal chromosome segregation, heightened aneuploidy (81-140 chromosomes), polyploidy, double minutes, dicentrics, chromatid exchanges, chromatid separations, pulverization, and chromosome markers were prominently noted. These abnormalities were intensified in cells pre-sensitized to 0.02 or 0.08 μg/ml cisplatin for seven days, then exposed to 0.03 or 0.1 μg/ml cisplatin for 24 hours, and finally cultured in cisplatin-free medium for 24 hours before chromosome analysis.
Conclusion: HeLa cells subjected to increasing concentrations of sub-toxic cisplatin exhibited large-scale, multiple-type abnormalities in nuclei, nucleoli, chromosomes, and chromosomal numbers, indicating genetic/chromosomal instability associated with high malignancy, before the development of cisplatin resistance. These results suggest that low doses of cisplatin administration in the clinical setting may promote malignancy and caution should be used with this type of treatment.
Copyright: © 2024 Delinassios et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Segregation of nucleolar components coincides with caspase-3 activation in cisplatin-treated HeLa cells.J Cell Sci. 2001 Feb;114(Pt 4):663-70. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.4.663. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11171371
-
Ectopic Tbx2 expression results in polyploidy and cisplatin resistance.Oncogene. 2008 Feb 7;27(7):976-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210701. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 17700536
-
DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK)-dependent cisplatin-induced loss of nucleolar facilitator of chromatin transcription (FACT) and regulation of cisplatin sensitivity by DNA-PK and FACT.Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Apr;7(4):581-91. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0049. Mol Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19372586
-
Analyses by comparative genomic hybridization of genes relating with cisplatin-resistance in ovarian cancer.Hum Cell. 2001 Dec;14(4):267-71. Hum Cell. 2001. PMID: 11925927 Review.
-
Chromosomal aberrations and genomic instability induced by topoisomerase-targeted antitumour drugs.Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2004 Jul;4(4):317-25. doi: 10.2174/1568011043352920. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2004. PMID: 15281904 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

