CTSG is a prognostic marker involved in immune infiltration and inhibits tumor progression though the MAPK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39724501
- PMCID: PMC11671429
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-024-06051-3
CTSG is a prognostic marker involved in immune infiltration and inhibits tumor progression though the MAPK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to investigate the biological roles and molecular mechanisms of Cathepsin G (CTSG) in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
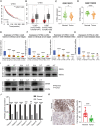
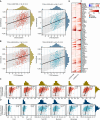
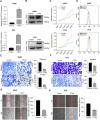
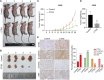
Methods: Western blotting and immunohistochemistry analyses of clinical samples were performed to determine the expression levels of CTSG in patients with NSCLC. Bioinformatic analysis of clinical datasets was conducted to evaluate the correlation between CTSG and lymph node metastasis, tumor stage, and immune cell infiltration. Gain-of-function assays and tumor implantation experiments were employed to determine the effects of CTSG on malignant behaviors of NSCLC cells. Transcriptome sequencing and subsequent bioinformatic analysis were performed to explore the signaling pathways regulated by CTSG. Western blotting and qPCR were utilized to assess the influence of CTSG on the MAPK and EMT signaling pathways.
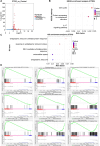
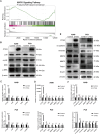
Results: CTSG is expressed at low levels and serves as a prognostic marker in NSCLC. The downregulation of CTSG expression was associated with lymph node metastasis, tumor stage, and immune cell infiltration. CTSG inhibits NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion as well as tumor growth in nude mice. There exists a significant correlation between CTSG expression and endoplasmic reticulum function, cell cycling, and the IL-17 signaling pathway. CTSG suppresses the MAPK and EMT signaling pathways in NSCLC cells. Moreover, DNA methylation and histone deacetylation have been identified as crucial mechanisms contributing to the decreased expression of CTSG.
Conclusion: CTSG inhibits NSCLC development by suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway and is also associated with tumor immunity.
Keywords: Biomarker; CTSG; MAPK; NSCLC; Prognostic.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: All experiments involved in clinical samples and animals were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Animal Experiments of Anhui Medical University.
Figures
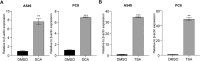
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

