A systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy of vasopressin as a vasoconstrictive and uterotonic drug in laparoscopic myomectomy
- PMID: 39724600
- PMCID: PMC11601973
- DOI: 10.4103/jmas.jmas_272_23
A systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy of vasopressin as a vasoconstrictive and uterotonic drug in laparoscopic myomectomy
Abstract
Introduction: Laparoscopic myomectomy is a commonly performed operation with fast recovery and excellent results. However, haemorrhagic nature of the operation mandates us to use variety of vasoconstrictive and uterotonic agents. Amongst which, one of them is vasopressin. It is a synthetic antidiuretic hormone analogue which has been in common use as a vasoconstrictive agent in various surgical procedures including laparoscopic myomectomy.
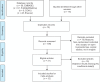
Methods: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials published from 2013 to 2023 (10 years) comparing the use of vasopressin against other drug or placebo or different doses of vasopressin was performed. The outcome measures were intraoperative blood loss, need for blood transfusion, difference in the haemoglobin (Hb) and haematocrit (Hct).
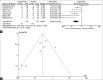
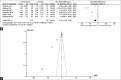
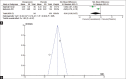
Results: We identified 176 articles through the study search, amongst which 12 articles were included for the meta-analysis. There was a significant heterogeneity in the studies with moderate risk of bias in eight studies and low risk of bias in four studies. Compared to placebo, vasopressin showed significantly lower odds need of blood transfusion (odds ratio [OR] 0.28, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.13-0.61, P = 0.002) and significantly lower pre-post fall in Hb (OR -3.12, 95% CI: -4.63--1.60, P < 0.0001). However, there was no statistically significant difference in intraoperative blood loss (OR -0.56 (95% CI: -2.04-0.92, P = 0.46) and pre-post fall in Hct (OR -0.94, 95% CI: -1.96-0.07, P > 0.05). Compared to other drug (epinephrine, misoprostol and octreotide acetate), vasopressin showed no significant superiority in controlling blood loss ( P > 0.05). Even the two doses of vasopressin (dilute vs. concentrated) showed no statistically significant difference between surgical blood loss and need for blood transfusion ( P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Vasopressin is an efficacious drug to be used for controlling blood loss, decreasing blood transfusion requirement and maintaining Hb and Hct during laparoscopic myomectomy.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Minimal Access Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Misoprostol vs vasopressin as a single hemostatic agent in laparoscopic myomectomy: Comparable, or just better than nothing?J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2020 Nov;46(11):2356-2365. doi: 10.1111/jog.14465. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2020. PMID: 32914544
-
Misoprostol for open myomectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised control trials.BJOG. 2021 Feb;128(3):476-483. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.16389. Epub 2020 Jul 28. BJOG. 2021. PMID: 32613769
-
Comparison of intramyometrial vasopressin plus rectal misoprostol with intramyometrial vasopressin alone to decrease blood loss during laparoscopic myomectomy: Randomized clinical trial.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018 Sep;228:279-283. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2018.07.006. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018. PMID: 30056355 Clinical Trial.
-
Dilute versus concentrated vasopressin administration during laparoscopic myomectomy: a randomised controlled trial.BJOG. 2017 Jan;124(2):262-268. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.14179. Epub 2016 Jun 30. BJOG. 2017. PMID: 27362908 Clinical Trial.
-
Pisat's Visual Vasopressor Injection Needle: A New Device for Increasing Patient Safety in Laparoscopic Myomectomy.J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2017 Dec;67(6):451-453. doi: 10.1007/s13224-017-1048-6. Epub 2017 Sep 12. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2017. PMID: 29162961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alomar O, Abu-Zaid A, Jamjoom MZ, Almubarki AA, Alsehaimi SO, Alabdrabalamir S, et al. Prophylactic vasopressin to reduce intraoperative blood loss and associated morbidities during myomectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 controlled trials. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2022;51:102485. - PubMed
-
- Protopapas A, Giannoulis G, Chatzipapas I, Athanasiou S, Grigoriadis T, Kathopoulis N, et al. Vasopressin during laparoscopic myomectomy: Does it really extend its limits? J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:441–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

