Utilization and regional disparities of radiotherapy in cancer treatment in Japan: a longitudinal study using NDB open data
- PMID: 39724924
- PMCID: PMC11753831
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrae100
Utilization and regional disparities of radiotherapy in cancer treatment in Japan: a longitudinal study using NDB open data
Abstract
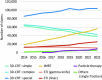
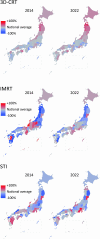
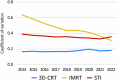
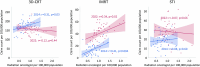
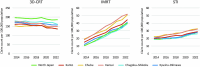
The National Database of Health Insurance Claims and Specific Health Checkups of Japan (NDB) is a database that stores anonymized information on medical receipts and health checkups in Japan. The NDB Open Data is a publicly accessible summary table of the NDB database. To reveal annual trends and regional disparities in radiotherapy utilization in Japan, we analyzed the NDB Open Data tables for a 9-year period from 2014 to 2022. We extracted medical cost codes for radiotherapy management fees and specific types of radiotherapy, such as stereotactic irradiation (STI) and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), to analyze nationwide changes over time. To investigate regional disparities, we counted the three subitems representing 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT), IMRT, and STI for each prefecture per year. The utilization of advanced radiotherapy techniques, such as IMRT (199% increase), increased, while the use of simpler forms of irradiation, such as 1 or 2-opposite fields irradiation (40% decrease), decreased in the period from 2014 to 2022. Regarding regional disparities, the coefficients of variation in 47 prefectures for 3D-CRT remained relatively stable at 0.17 in 2014 and 0.18 in 2022, while the coefficients of variation for IMRT and STI decreased from 0.64 and 0.39 in 2014 to 0.31 and 0.36 in 2022, respectively. The popularization of IMRT was correlated with the number of certified radiation oncologists in the prefecture. In conclusion, although the utilization of high-precision radiotherapy in Japan has been increasing and regional differences have been diminishing, there are still persistent disparities.
Keywords: IMRT; NDB open data; STI; radiotherapy; regional disparity.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests on this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current situation and trends of radiation therapy in Japan based on the National Database Open Data.J Radiat Res. 2024 Dec 3;65(6):864-871. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrae078. J Radiat Res. 2024. PMID: 39390811 Free PMC article.
-
Regional disparities in IMRT utilization in Japan: analysis of trends and associated medical resources from 2015 to 2019†.J Radiat Res. 2025 May 23;66(3):290-295. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraf024. J Radiat Res. 2025. PMID: 40364526 Free PMC article.
-
[Medical expenses for diabetes care in Japan: Analysis of inter-prefecture differences].Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi. 2020;67(8):501-508. doi: 10.11236/jph.67.8_501. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi. 2020. PMID: 32879236 Japanese.
-
Stroke Research Using Administrative Claims Database in Japan: A Narrative Review.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024 Oct 1;31(10):1341-1352. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV22022. Epub 2024 Aug 3. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024. PMID: 39098041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in radiation oncology: intensity-modulated radiotherapy, a clinical perspective.Int J Clin Oncol. 2014 Aug;19(4):564-9. doi: 10.1007/s10147-014-0718-y. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24981775 Review.
References
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare . National Database of Health Insurance Claims and Specific Health Checkups of Japan. Japan: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/iryouhoken... (16 July 2024, date last accessed).
-
- Ministry of Health . Labour and Welfare. NDB Open Data. Japan: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/0000177182.html (16 July 2024, date last accessed).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

