[AKBA combined with doxorubicin inhibits proliferation and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and xenograft growth in nude mice]
- PMID: 39725635
- PMCID: PMC11683345
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.22
[AKBA combined with doxorubicin inhibits proliferation and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and xenograft growth in nude mice]
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the synergistic inhibitory effects of AKBA and doxorubicin on malignant phenotype of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) MDA-MB-231 cells.
Methods: CCK-8 assay was used to determine the 48-h IC50 of AKBA and doxorubicin in MDA-MB-231 cells, and SynergyFinder was employed to calculate the synergistic index and the optimal concentrations of the two agents. MDA-MB-231 cells treated with AKBA (22.5 μmol/L), doxorubicin (0.84 μmol/L) or their combination were examined for changes in cell proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis using Transwell migration, scratch assay, clone generation, RT-qPCR and Western blotting. Network pharmacology analysis was conducted to identify the downstream targets of AKBA in TNBC. In nude mouse models bearing subcutaneous MDA-MB-231 cell xenografts, the effects of normal saline, AKBA (50 mg/kg), doxorubicin (2.5 mg/kg), and AKBA combined with doxorubicin on xenograft growth and histopathology were observed.
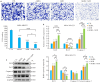
Results: The IC50 of AKBA and doxorubicin in MDA-MB-231 cells at 48 h was 45.15±0.97 μmol/L and 0.42±0.99 μmol/L, respectively. SynergyFinder confirmed the synergistic effect of AKBA and ADR with a ZIP>10. The combined treatment with AKBA and doxorubicin significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion, promoted apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 cells, and effectively suppressed xenograft growth in nude mice. Network pharmacology analysis predicted that AKBA affects the progression of TNBC through its downstream target AKBA.
Conclusions: AKBA combined with doxorubicin inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion, promotes apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 cells and suppresses MDA-MB-231 cell xenograft growth in nude mice. The combined use of AKBA can attenuate the toxic effects of doxorubicin in nude mice.
目的: 探究AKBA联合阿霉素对三阴性乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231在增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡上的协同抑制作用,并通过网络药理学分析AKBA作用乳腺癌的下游信号通路。方法: MDA-MB-231细胞体外培养,CCK-8法分别检测AKBA和阿霉素(ADR)作用MDA-MB-231细胞48 h的半抑制浓度(IC50),SynergyFinder在线网站( https://synergyfinder.fimm.fi )分析AKBA联合阿霉素的协同指数和最佳协同浓度。设置实验分组,对照组:MDA-MB-231正常培养;AKBA组:MDA-MB-231+AKBA(22.5 μmol/L)处理48 h;ADR组:MDA-MB-231+(0.84 μmol/L)处理48 h;AKBA+ADR组:MDA-MB-231+AKBA(22.5 μmol/L)+ADR(0.84 μmol/L)处理48 h,使用克隆形成实验、Transwell迁移和侵袭、划痕实验检测AKBA联合阿霉素抑制细胞迁移和侵袭的能力,采用Western blotting和qPCR实验检测凋亡相关基因的表达情况,将4~5周龄Balb/c nude小鼠随机分为4组(6只/组),建立裸鼠异种移植瘤模型,对照组:腹腔注射200 μL 0.9%生理盐水;AKBA组:腹腔注射200 μL50 mg/kg的AKBA;ADR组:腹腔注射200 μL 2.5 mg/kg的ADR;AKBA+ADR组:腹腔注射200 μL50 mg/kg的AKBA和2.5 mg/kg的ADR等量混合溶液,检测各组抑瘤率,HE染色检测组织病理情况,并通过网络药理学分析预测AKBA作用于乳腺癌的下游靶点和信号通路。结果: AKBA对MDA-MB-231细胞作用48 h的IC50为45.15±0.97 μmol/L,ADR的IC50为0.42±0.99 μmol/L;SynergyFinder证实AKBA与ADR联合具有协同作用(ZIP>10);相较于对照组、AKBA组和阿霉素组,AKBA+ADR组明显抑制TNBC细胞增殖活性(P<0.0001),集落形成数量减少更多(P<0.05);相较对照组、AKBA和ADR组,AKBA+ADR组明显减弱细胞划痕愈合率(P<0.01);较对照组、AKBA组和ADR组,AKBA+ADR组所致细胞迁移至下室的数量减少更多(P<0.01);与对照组和AKBA或ADR单独使用相比,AKBA+ADR组抑制MDA-MB-231细胞侵袭基质胶能力增强(P<0.05);较AKBA或ADR单独作用,AKBA+ADR组在mRNA和蛋白水平上调Bax、Caspase-3剪切体和下调Bcl-2的表达更多(P<0.05);AKBA组、ADR组和AKBA+ADR组的抑瘤率分别为23.80%、52.73%和81.83%(P<0.01),AKBA+ADR组相比于ADR组对小鼠脏器造成的毒性损伤更小;网络药理学预测AKBA通过PTGS2影响乳腺癌进展。结论: AKBA联合阿霉素能够显著抑制TNBC细胞MDA-MB-231的增殖、迁移和侵袭,并促进细胞凋亡,在裸鼠体内抑制移植瘤生长并减轻阿霉素的毒性作用。.
Keywords: AKBA; acetyl-11-keto‑β‑boswellic acid; doxorubicin; triple-negative breast cancer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Excellent effects and possible mechanisms of action of a new antibody-drug conjugate against EGFR-positive triple-negative breast cancer.Mil Med Res. 2021 Dec 9;8(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s40779-021-00358-9. Mil Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34879870 Free PMC article.
-
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound combined with microbubble mediated JNK/c-Jun pathway to reverse multidrug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 8;14(1):27250. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78272-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39516537 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane induces autophagy by inhibition of HDAC6-mediated PTEN activation in triple negative breast cancer cells.Life Sci. 2018 Nov 15;213:149-157. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.10.034. Epub 2018 Oct 20. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30352240
-
Cordycepin Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Doxorubicin in Treating Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 27;25(13):7077. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137077. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000182 Free PMC article.
-
Cantharidin Inhibits the Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Suppressing Autophagy and Inducing Apoptosis in Vitro and in Vivo.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(5):1829-1840. doi: 10.1159/000484069. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29050003
References
-
- Keenan TE, Tolaney SM. Role of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2020, 18(4): 479-89. - PubMed
-
- Kwakman JJM, Bond MJG, Demichelis RM, et al. . Adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with clinically node-negative but pathologically node-positive rectal cancer in the Netherlands: a retrospective analysis[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2024, 197: 113466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
