[PHPS1 enhances PD-L1 serine phosphorylation by regulating ROS/SHP-2/AMPK activity to promote apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells]
- PMID: 39725637
- PMCID: PMC11683339
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.24
[PHPS1 enhances PD-L1 serine phosphorylation by regulating ROS/SHP-2/AMPK activity to promote apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells]
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the mechanism of PHPS1 for promoting apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells and the role of AMPK in regulating tumor angiogenesis under hypoxic conditions.
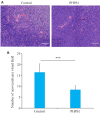
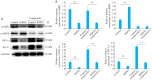
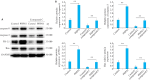
Methods: Human oral squamous cell carcinoma Ca9-22 cells cultured in hypoxic conditions (1% O2) were inoculated subcutaneously in 16 nude mice, which were divided into control group and PHPS1 group (n=8) for treatment with 10% DMSO and 10% PHPS1 respectively. Tumor growth in the mice was monitored till 14 days after the treatment, and the xenografts were examined pathologically using HE staining. In Ca9-22 cells cultured in 1% O2, the effect of PHPS1, compound C (an AMPK inhibitor), and their combination on expressions of SHP-2, AMPK, HIF-1α, PD-L1, caspase-8, caspase-3 and BAX were evaluated using Western blotting.
Results: In the tumor-bearing nude mice, PHPS1 treatment significantly inhibited tumor growth and neovascularization. HE staining showed significantly reduced tumor angiogenesis in PHPS1-treated mice. In Ca9-22 cells in hypoxic cultures, PHPS1 treatment significantly decreased the expression levels of SHP-2, HIF-1α, PD-L1, ERK2, STAT3 and VEGF and increased the expression of AMPK. The inhibitory effects of PHPS1 on HIF-1α and PD-L1 were obviously attenuated by the addition of compound C. PHPS1 also enhanced the expressions of caspase-3, caspase-8 and Bax proteins and increased the phosphorylation levels of PD-L1 and S195 in Ca9-22 cells, and these effects were effectively attenuated by compound C.
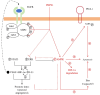
Conclusions: PHPS1 can enhance PD-L1 serine phosphorylation by regulating SHP-2/AMPK activity to promote apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells under hypoxic conditions.
目的: 探讨PHPS1通过对口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞ROS/酪氨酸磷酸酶SHP-2/AMPK活性进而促进PD-L1丝氨酸磷酸化进而加速肿瘤凋亡的机制研究,分析腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMPK)对于低氧环境下肿瘤内血管生成的影响。方法: 6~8周龄健康裸鼠16只,皮下移植瘤模型分为Control组和PHPS1组,8只/组,培育14 d后观察肿瘤的生长情况,并将其切片进行HE染色固定并拍照。将人口腔鳞状细胞癌Ca9-22细胞系培养后分为Control组、PHPS1组、Control+Compound C组(Compound C为AMPK抑制剂)、PHPS1+Compound C组在1%低氧环境下培养,通过Western blotting对细胞内SHP-2、AMPK、HIF-1α、PD-L1、caspase-8、caspase-3和BAX含量进行检测。结果: 裸鼠成瘤与血管新生实验结果显示PHPS1抑制了裸鼠体内肿瘤生长和血管新生(P<0.05)。Western blotting分析显示PHPS1降低了SHP-2、HIF-1α、PD-L1、ERK2、STAT3和VEGF的表达,同时增加了AMPK的表达(P<0.05)。加入AMPK抑制剂后,PHPS1对HIF-1α和PD-L1的抑制作用减弱(P<0.05)。此外,PHPS1促进了caspase-3、caspase-8、PD-L1 S195磷酸化和Bax蛋白的表达,这些效应在加入AMPK抑制剂后也有所减弱(P<0.05)。HE染色结果表明PHPS1组肿瘤血管生成数量减少(P<0.01)。结论: 在缺氧环境下可以通过调节SHP-2/AMPK活性进而促进PD-L1丝氨酸磷酸化进而加速肿瘤凋亡。.
Keywords: PD-L1; SHP-2; mitogen-activated protein kinase; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures



References
-
- Grégoire V, Grau C, Lapeyre M, et al. . Target volume selection and delineation (T and N) for primary radiation treatment of oral cavity, oropharyngeal, hypopharyngeal and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oral Oncol, 2018, 87: 131-7. - PubMed
-
- Porceddu SV, Daniels C, Yom SS, et al. . Head and neck cancer international group (HNCIG) consensus guidelines for the delivery of postoperative radiation therapy in complex cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (cSCCHN)[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2020, 107(4): 641-51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
