Epigallocatechin-3-gallate therapeutic potential in human diseases: molecular mechanisms and clinical studies
- PMID: 39725830
- PMCID: PMC11671467
- DOI: 10.1186/s43556-024-00240-9
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate therapeutic potential in human diseases: molecular mechanisms and clinical studies
Abstract
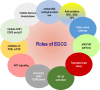
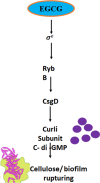
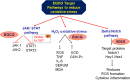
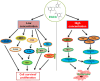
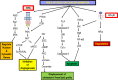
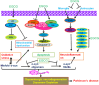
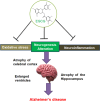
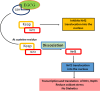
Green tea has garnered increasing attention across age groups due to its numerous health benefits, largely attributed to Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), its key polyphenol. EGCG exhibits a wide spectrum of biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anticancer, and neuroprotective properties, as well as benefits for cardiovascular and oral health. This review provides a comprehensive overview of recent findings on the therapeutic potential of EGCG in various human diseases. Neuroprotective effects of EGCG include safeguarding neurons from damage and enhancing cognitive function, primarily through its antioxidant capacity to reduce reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated during physiological stress. Additionally, EGCG modulates key signaling pathways such as JAK/STAT, Delta-Notch, and TNF, all of which play critical roles in neuronal survival, growth, and function. Furthermore, EGCG is involved in regulating apoptosis and cell cycle progression, making it a promising candidate for the treatment of metabolic diseases, including cancer and diabetes. Despite its promising therapeutic potential, further clinical trials are essential to validate the efficacy and safety of EGCG and to optimize its delivery to target tissues. While many reviews have addressed the anticancer properties of EGCG, this review focuses on the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways by which EGCG used in specific human diseases, particularly cancer, neurodegenerative and metabolic diseases. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers, clinicians, and healthcare professionals, revealing the potential of EGCG in managing neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, and metabolic diseases and highlighting its broader therapeutic values.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Epigallocatechin gallate; Natural products; Neuroinflammation; Neurological disorders; Targeted therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigallocatechin 3-gallate-induced neuroprotection in neurodegenerative diseases: molecular mechanisms and clinical insights.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun;480(6):3363-3383. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05211-4. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39832108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG): Pharmacological Properties, Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potential.Molecules. 2025 Feb 1;30(3):654. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030654. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Dec 15;82(12):1807-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.07.093. Epub 2011 Jul 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21827739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of EGCG: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016 Aug;26(8):907-16. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2016.1203419. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016. PMID: 27338088 Review.
-
Health Benefits of Epigallocatechin Gallate and Forskolin with a Special Emphasis on Glaucoma and Other Retinal Diseases.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Nov 27;60(12):1957. doi: 10.3390/medicina60121957. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39768839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on the Protective Effect of Green Tea Polyphenol (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) on the Liver.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 21;17(7):1101. doi: 10.3390/nu17071101. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40218859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catechins and Human Health: Breakthroughs from Clinical Trials.Molecules. 2025 Jul 25;30(15):3128. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153128. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The green tea component (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects against cytokine-induced epithelial barrier damage in intestinal epithelial cells.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 14;16:1559812. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1559812. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40438590 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of potential of natural compounds to regulate epigenetic modifications in colorectal cancer: a recent update.Epigenetics. 2025 Dec;20(1):2491316. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2025.2491316. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 40239010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Green Tea and Its Bioactive Compounds on Mood Disorder Symptomology and Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 7;13(7):1656. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071656. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722728 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fraga CG, Croft KD, Kennedy DO, Tomás-Barberán FA. The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health. Food Funct. 2019;10(2):514–28. 10.1039/C8FO01997E. - PubMed
-
- Zhang S, Mao B, Cui S, Zhang Q, Zhao J, Tang X, et al. Absorption, metabolism, bioactivity, and biotransformation of epigallocatechin gallate. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(19):6546–66. 10.1080/10408398.2023.2170972. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T, Miyoshi N, Hayakawa S, Imai S, Isemura M, Nakamura Y. Health benefits of tea consumption. Beverage impacts on health and nutrition. Springer; 2016. p. 49–67. 10.1007/978-3-319-23672-8_4
-
- Hayakawa S, Oishi Y, Tanabe H, Isemura M, Suzuki Y. Tea, Coffee and Health Benefits. Bioactive Molecules in Food; Mérillon, J-M, Ramawat, KG, Eds. 2018:1–58. 10.3390/molecules25194553
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
