Rhaponticin Alleviates Collagen-induced Arthritis by Inhibiting NLRP3/GSDMD-mediated Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
- PMID: 39725843
- PMCID: PMC12336096
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-024-02228-7
Rhaponticin Alleviates Collagen-induced Arthritis by Inhibiting NLRP3/GSDMD-mediated Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
Abstract
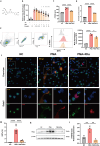
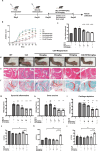
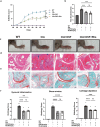
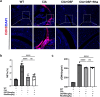
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) play an important role in the inflammatory response and progressive joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Rhaponticin (Rha) is a stilbene glycoside compound with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic potential of Rha in RA, with a specific focus on its effects on NETs and on the underlying mechanisms of Rha. NETs formation induced by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model were implemented to evaluate the pharmacological effects of Rha in vitro and in vivo. The potential mechanism of Rha in improving RA was screened and verified using the SuperPred and DisGeNET databases. Disulfiram (a GSDMD inhibitor) and S100a8cre GSDMDfl/fl mice were used to confirm whether GSDMD is key to the role of Rha. The findings demonstrate that Rha significantly inhibited reactive oxygen species and NETs production in PMA-activated neutrophils. In vivo, Rha treatment significantly relieved joint symptoms in CIA mice and NETs production. Mechanistically, Rha reduced NETs production via inhibition of NLRP3/GSDMD activation. Neutrophil-specific GSDMD depletion eliminated the effects of Rha on NETs production in vitro. Disulfiram eliminated the effects of Rha on the inhibition of NETs production and alleviated joint inflammation in mice in vivo and in vitro. Overall, our results indicated that Rha exerts a protective effect against CIA by inhibiting NETs production through the NLRP3/GSDMD pathway. The results of this study provide new strategies for treating RA.
Keywords: Gasdermin-D; Neutrophil extracellular traps; Rhaponticin; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: This study was approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Yangzhou University (approval no. 202401015) and was conducted in accordance with the National Research Council guidelines and the Ethics Committee. Competing Interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Chak Sing, L., C. Faith, D. Leonila, H. Andrew, H. Tsu Yi, J. Rahul, J. Seung Min, K. Mitsumasa, K. Ashok, L. Khai Pang, et al. 2019. 2018 update of the APLAR recommendations for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 22: 357–375. 10.1111/1756-185x.13513. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sherbini, A.A., J.M. Gwinnutt, K.L. Hyrich, and S.M.M. Verstappen. 2022. Rates and predictors of methotrexate-related adverse events in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a nationwide UK study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 61: 3930–3938. 10.1093/rheumatology/keab917. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

