Comparative analysis of the LEA gene family in seven Ipomoea species, focuses on sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.)
- PMID: 39725899
- PMCID: PMC11670493
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05981-x
Comparative analysis of the LEA gene family in seven Ipomoea species, focuses on sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.)
Abstract
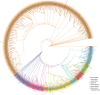
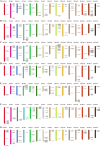
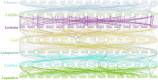
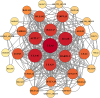
Late Embryogenesis Abundant (LEA) proteins are extensively distributed among higher plants and are crucial for regulating growth, development, and abiotic stress resistance. However, comprehensive data regarding the LEA gene family in Ipomoea species remains limited. In this study, we conducted a genome-wide comparative analysis across seven Ipomoea species, including sweet potato (I. batatas), I. trifida, I. triloba, I. nil, I. purpurea, I. cairica, and I. aquatica, identifying 73, 64, 77, 62, 70, 70, and 74 LEA genes, respectively. The LEA genes were divided into eight subgroups: LEA_1, LEA_2, LEA_3, LEA_4, LEA_5, LEA_6, SMP, and Dehydrin according to the classification of the LEA family in Arabidopsis. Gene structure and protein motif analyses revealed that genes within the same phylogenetic group exhibited comparable exon/intron structures and motif patterns. The distribution of LEA genes across chromosomes varied among the different Ipomoea species. Duplication analysis indicated that segmental and tandem duplications significantly contributed to the expansion of the LEA gene family, with segmental duplications being the predominant mechanism. The analysis of the non-synonymous (Ka) to synonymous (Ks) ratio (Ka/Ks) indicated that the duplicated Ipomoea LEA genes predominantly underwent purifying selection. Extensive cis-regulatory elements associated with stress responses were identified in the promoters of LEA genes. Expression analysis revealed that the LEA gene exhibited widespread expression across diverse tissues and showed responsive modulation to various abiotic stressors. Furthermore, we selected 15 LEA genes from sweet potatoes for RT-qPCR analysis, demonstrating that five genes responded to salt stress in roots, while three genes were responsive to drought stress in leaves. Additionally, expression changes of seven genes varied at different stages of sweet potato tuber development. These findings enhanced our understanding of the evolutionary dynamics of LEA genes within the Ipomoea genome and may inform future molecular breeding strategies for sweet potatoes.
Keywords: Ipomoea species; LEA gene family; Abiotic stress; Gene expression; Sweet potato.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The sweet potato materials used in this study were obtained from the College of Coastal Agriculture Sciences, Guangdong Ocean University, Guangdong Province, China. The collection and utilization of sweet potato materials, as well as the methods employed in this study, adhere to the guidelines and regulations set forth by relevant institutions and national and international standards. Consent to publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


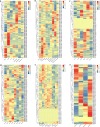
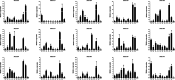
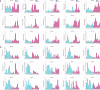
References
-
- Ahuja I, de Vos RC, Bones AM, Hall RD. Plant molecular stress responses face climate change. Trends Plant Sci. 2010;15(12):664–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

