Protein kinase CK2 sustains de novo fatty acid synthesis by regulating the expression of SCD-1 in human renal cancer cells
- PMID: 39726006
- PMCID: PMC11674369
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03611-y
Protein kinase CK2 sustains de novo fatty acid synthesis by regulating the expression of SCD-1 in human renal cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is a type of cancer characterized by a vast intracellular accumulation of lipids that are critical to sustain growth and viability of the cells in the tumour microenvironment. Stearoyl-CoA 9-desaturase 1 (SCD-1) is an essential enzyme for the synthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids and consistently overexpressed in all stages of ccRCC growth.
Methods: Human clear cell renal cell carcinoma lines were treated with small-molecule inhibitors of protein kinase CK2. Effects on the expression levels of SCD-1 were investigated by RNA-sequencing, RT-qPCR, Western blot, and in vivo studies in mice. Phase-contrast microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, and MALDI-mass spectrometry analysis were carried out to study the effects on endogenous lipid accumulation, induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress, rescue effects induced by exogenous MUFAs, and the identity of lipid populations. Cell proliferation and survival were investigated in real time employing the Incucyte® live-cell analysis system. Statistical significance was determined by applying the two-tailed Student's t test when comparing two groups of data whereas the two-way ANOVA, multiple Tukey's test was employed for multiple comparisons.
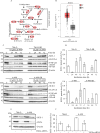
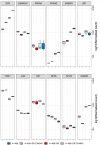
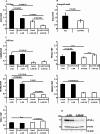
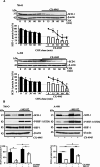
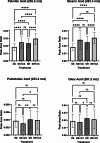
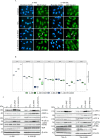
Results: Here, we show that protein kinase CK2 is critical for preserving the expression of SCD-1 in ccRCC lines maintained in culture and heterotransplanted into nude mice. Consistent with this, pharmacological inhibition of CK2 leads to induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress linked to unfolded protein response activation and decreased proliferation of the cells. Both effects could be reversed by supplementing the growth medium with oleic acid indicating that these effects are specifically caused by reduced expression of SCD-1. Analysis of lipid composition by MALDI-mass spectrometry revealed that inhibition of CK2 results in a significant accumulation of the saturated palmitic- and stearic acids.
Conclusions: Collectively, our results revealed a previously unidentified molecular mechanism regulating the synthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids corroborating the notion that novel therapeutic approaches that include CK2 targeting, may offer a greater synergistic anti-tumour effect for cancers that are highly dependent on fatty acid metabolism.
Keywords: CK2; Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; SCD-1; fatty acids; sunitinib.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Studies involving experimental animals were approved by the Danish Animal Experiments Inspectorate (permission nr.: 2022-15-0201-01265). Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Abramczyk H, Surmacki J, Kopec M, Olejnik AK, Lubecka-Pietruszewska K, Fabianowska-Majewska K. The role of lipid droplets and adipocytes in cancer. Raman imaging of cell cultures: MCF10A, MCF7, and MDA-MB-231 compared to adipocytes in cancerous human breast tissue. Analyst. 2015;140:2224–35. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

