Tumor Lysis Syndrome in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated With a Venetoclax Based Regimen
- PMID: 39726154
- PMCID: PMC11880964
- DOI: 10.1111/ejh.14371
Tumor Lysis Syndrome in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated With a Venetoclax Based Regimen
Abstract
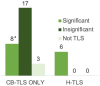
Venetoclax with hypomethylating agents (HMA) is the standard of care for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in patients ineligible for intensive chemotherapy and is associated with tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). TLS prophylaxis and the use of Cairo Bishop versus Howard diagnostic criteria are not standardized. Here we report TLS prophylaxis and incidence in a retrospective cohort of 100 consecutive AML patients treated with venetoclax and HMA. Thirty four patients developed laboratory Cairo Bishop TLS; 8 of these met criteria for clinical Cairo Bishop TLS. Only 6 of patients met Howard TLS criteria. Fourteen patients had spontaneous TLS. Ninety two out of 100 patients had a white blood cell count (WBC) < 25 000 cells/μL at treatment start. Prophylaxis like the original venetoclax trial with allopurinol (56%), intravenous fluids (21%), and frequent lab monitoring (56%) was less common. There was a trend toward increased Cairo Bishop TLS in patients with WBC ≥ 15 000 cells/μL. In our study Howard TLS criteria better identified patients with significant TLS. Aggressive TLS prophylaxis was uncommon in our cohort and is likely unnecessary for most patients at low risk of TLS.
Keywords: Leukoreduction; Venetoclax; acute myeloid leukemia; prophylaxis; tumor lysis syndrome.
© 2024 The Author(s). European Journal of Haematology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
MR, DB, EH, RH, NH, AL, SM, AM, MEM, VRP: None. MC: Cartography Bioscences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. NF: Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Sana Biotechnology: Consultancy. SG: Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Carisma Therapeutics: Current equity holder in publicly‐traded company, Current holder of stock options in a privately‐held company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties: patents, Research Funding; Interius Biotherapeutics: Current equity holder in private company, Current holder of stock options in a privately‐held company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Asher: Research Funding; Currus: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Inndura: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mission Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; NKILT: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Vor Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. CL: Novartis: Consultancy; Rigel: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Daiichi: Consultancy; Taiho: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy, Research Funding. SL: Onconova: Research Funding; Bristol‐Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Marker Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy; Astellas: Honoraria. IM: Garuda Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding. AP: Forma: Consultancy; Rigel: Honoraria; Actinium: Honoraria; Aptose: Honoraria; BerGen Bio: Honoraria; Genentech: Honoraria; Foghorn: Consultancy; FujiFilm: Research Funding; Syndax: Research Funding; Immunogen: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Beat AML: Other: Participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board; Bayer: Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Daiichi‐Sankyo: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. DP: Sana Therapeutics: Consultancy, Current equity holder in publicly‐traded company; Tmunity: Patents & Royalties; Wiley and Sons Publishing: Honoraria; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; National Marrow Donor Program: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mirror Biologics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite/Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Current equity holder in publicly‐traded company; DeCart: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Capstan Bio: Honoraria; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bluebird Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Angiocrine Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. KP: Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astra Zeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz Pharamceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol‐Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding. ES: Amgen: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; genmab: Consultancy.
Figures




References
-
- National Cancer Institute Surveillance Epidemiology, Program ER , “Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia—Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML),” 2022, https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html.
-
- Konopleva M., Pollyea D. A., Potluri J., et al., “Efficacy and Biological Correlates of Response in a Phase II Study of Venetoclax Monotherapy in Patients With Acute Myelogenous Leukemia,” Cancer Discovery 6, no. 10 (2016): 1106–1117, 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0313. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

