Ceramide-based risk score CERT-1 improves risk prediction for overall mortality and adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with and without cardiovascular disease: A prospective cohort study
- PMID: 39726197
- PMCID: PMC11802398
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.16156
Ceramide-based risk score CERT-1 improves risk prediction for overall mortality and adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with and without cardiovascular disease: A prospective cohort study
Abstract
Aims: Whether the plasma-based ceramide-based risk score CERT1 improves risk prediction for cardiovascular disease (CVD) is uncertain.
Materials and methods: Baseline and follow-up data were combined from two cohorts, 334 patients with established/suspected CVD and 196 patients with type 2 diabetes followed for a median of 74 months (interquartile range 54-79 months). For the calculation of CERT1 risk score, we measured four specific plasma ceramides [Cer(d18:1/16:0), Cer(d18:1/18:0) and Cer(d18:1/24:1)] and their ratios to Cer(d18:1/24:0). Based on the CERT1 risk score, patients were split into four risk categories (low, moderate, increased or high risk). The primary outcome was a composite of overall mortality and incident nonfatal CVD outcomes (including myocardial infarction, ischaemic stroke or permanent atrial fibrillation).
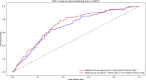
Results: One hundred and thirty-nine patients developed the primary composite outcome (72 nonfatal CVD outcomes and 67 total deaths) during follow-up. Baseline CERT1 risk categories were significantly associated with the risk of developing the primary composite outcome (adjusted HR for high vs. low-risk category 2.43, 95% CI 1.39-4.22, p = 0.002, and adjusted HR for increased vs. low-risk category 2.16, 95% CI 1.28-3.63, p = 0.004). Receiver operator characteristic curve analysis showed that adding CERT1 risk score to traditional CVD risk factors and pre-existing CVD, improved the discriminatory capability of the regression model for predicting the primary composite outcome (AUROC 0.691 [95% CI 0.674-0.769] vs. 0.722 [95% CI 0.642-0.742], p = 0.0275).
Conclusions: The ceramide-based risk score CERT1 risk score improves risk prediction for long-term risk of overall mortality and adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with and without CVD.
Keywords: CERT1 score; CVD; cardiovascular morbidity; mortality; plasma ceramides.
© 2024 The Author(s). Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Basal and post-stress ceramide-based risk score CERT1 predicts all-cause mortality and nonfatal myocardial infarction in patients with suspected or established coronary artery disease undergoing stress myocardial perfusion scintigraphy.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2025 Feb;35(2):103735. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2024.09.005. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2025. PMID: 39428276
-
Plasma Ceramides Predict All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Apr 22;110(5):1497-1504. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae388. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 38849301
-
A new plasma ceramide 24-based risk score predicts overall mortality and nonfatal myocardial infarction in patients with suspected or known coronary artery disease.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2025 Jun 21:104206. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2025.104206. Online ahead of print. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2025. PMID: 40685265
-
Ceramides and risk of major adverse cardiovascular events: A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies.J Clin Lipidol. 2020 Mar-Apr;14(2):176-185. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2020.01.005. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Clin Lipidol. 2020. PMID: 32067904 Review.
-
Ceramides and Ceramide Scores: Clinical Applications for Cardiometabolic Risk Stratification.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Sep 29;11:570628. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.570628. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33133018 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Edsfeldt A, Dunér P, Ståhlman M, et al. Sphingolipids contribute to human atherosclerotic plaque inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016;36(6):1132‐1140. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Tham WK, Lee J, et al. Plasma ceramides predict all‐cause and cause‐specific mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024:dgae388. https://doi/org/10.1210/clinem/dgae388. Epub ahead of print. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

