Functional interaction of melatonin with gasotransmitters and ROS in plant adaptation to abiotic stresses
- PMID: 39726429
- PMCID: PMC11669522
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1505874
Functional interaction of melatonin with gasotransmitters and ROS in plant adaptation to abiotic stresses
Abstract
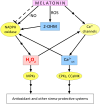
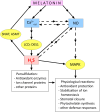
Melatonin is considered a multifunctional stress metabolite and a novel plant hormone affecting seed germination, root architecture, circadian rhythms, leaf senescence, and fruit ripening. Melatonin functions related to plant adaptation to stress stimuli of various natures are considered especially important. One of the key components of melatonin's stress-protective action is its ability to neutralise reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species directly. However, many of its effects are related to its involvement in the signalling network of plant cells and its influence on the expression of a large number of genes important for adaptation to adverse factors. Insights into the functional relationships of melatonin with gasotransmitters (GT) - gaseous molecules performing signalling functions - are still emerging. This review has analysed and summarised the experimental data that testify to the participation of the main GTs - nitric oxide, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon monoxide - in the implementation of the protective effect of melatonin when plants are exposed to abiotic stimuli of various nature. In addition, modulation by melatonin of one of the most important components in the action of GTs and ROS - post-translational modifications of proteins and the influence of ROS and GTs on melatonin synthesis in plants under stress conditions and the specific physiological effects of exogenous melatonin and GTs have been reviewed. Finally, the prospects of the GTs' practical application to achieve synergistic stress-protective effects on plants have been considered.
Keywords: ROS; abiotic stress; carbon monoxide; cell signalling; hydrogen sulfide; melatonin; nitric oxide; protein post-translational modifications.
Copyright © 2024 Kolupaev, Yemets, Yastreb and Blume.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




References
-
- Agathokleous E., Zhou B., Xu J., Ioannou A., Feng Z., Saitanis C. J., et al. (2021). Exogenous application of melatonin to plants, algae, and harvested products to sustain agricultural productivity and enhance nutritional and nutraceutical value: A meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 200, 111746. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111746 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aghdam M. S., Luo Z., Jannatizadeh A., Sheikh-Assadi M., Sharafi Y., Farmani B., et al. (2019). Employing exogenous melatonin applying confers chilling tolerance in tomato fruits by upregulating ZAT2/6/12 giving rise to promoting endogenous polyamines, proline, and nitric oxide accumulation by triggering arginine pathway activity. Food Chem. 275, 549–556. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.157 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahammed G. J., Xu W., Liu A., Chen S. (2019). Endogenous melatonin deficiency aggravates high temperature-induced oxidative stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. Environ. Exp. Bot. 161, 303–311. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.06.006 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

