Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Methotrexate-Induced Gonadal Damage in Rats: Role of SCF, mTOR, and SIRT-1
- PMID: 39726526
- PMCID: PMC11683295
- DOI: 10.4274/MMJ.galenos.2024.04932
Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Methotrexate-Induced Gonadal Damage in Rats: Role of SCF, mTOR, and SIRT-1
Abstract
Objective: Methotrexate (MTX) is a highly effective chemotherapy for cancer. This drug has a gonadotoxic effect, mainly in the testes and ovaries. Our study used histopathological and immunohistochemical methods to assess the potential damage to testicular and ovarian tissue caused by MTX use.
Methods: Twenty-four Wistar albino rats, both male and female, were used in our study. Four sets of rats; control male, MTX male, control female, and MTX female were created. The male and female MTX-treated groups received a single intraperitoneal dose of 20 mg/kg MTX. The testes and ovaries of rats sacrificed under general anesthesia were extracted and histopathologically analyzed. In addition, the immunoreactivity intensities of stem cell factor (SCF), mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), and SIRT-1 in both tissues were measured by immunohistochemistry.
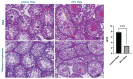
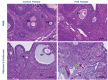
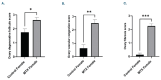
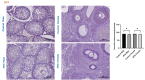
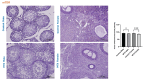
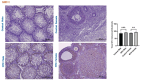
Results: Johnsen's testicular biopsy score in the testicular seminiferous tubules was significantly lower in the MTX group than in the control group (p<0.001). The ovary showed substantial follicular degeneration (p<0.05), vascular congestion (p<0.01), and fibrosis (p<0.001). MTX reduced SCF immunoreactivity density in the testis and ovary (p<0.05). Furthermore, MTX reduced mTOR, a marker of autophagy, in the testis (p<0.05) and ovary (p<0.001) compared with the control. SIRT-1 intensity increased dramatically in the testis (p<0.001) and ovary (p<0.01) in the injured group, unlike the mTOR marker.
Conclusions: Our investigation revealed that the gonads incurred significant damage as a result of MTX. One vital option for reducing or eliminating this damage to the ovaries and testicles is the use of anti-oxidant-rich substances.
Amaç: Metotreksat (MTX) kanser olgularının önde gelen kemotörapatiklerinden biridir. Bu ilaç özellikle testis ve ovaryum üzerinde gonadotoksik bir etkiye sahiptir. Çalışmamızın amacı MTX kullanımına bağlı testis ve ovaryum dokusunda oluşabilecek olası hasarı histopatolojik ve immünohistokimyasal analizlerle araştırmaktır.
Yöntemler: Çalışmamız için 24 adet Wistar albino erkek ve dişi sıçanlar kullanıldı. Bu sıçanlar 4 farklı gruba ayrıldı. Bu gruplar; kontrol erkek, MTX erkek, kontrol dişi ve MTX dişi olarak isimlendirildi. MTX uygulanan erkek ve dişi grubuna 20 mg/kg MTX, tek doz ve intraperitoneal olarak uygulandı. Genel anestezi altında sakrifiye edilen sıçanların testis ve ovaryumları alınarak histopatolojik analizler için kullanıldı. Ayrıca her iki dokuda da kök hücre faktörü (SCF), rapamisinin mekanistik hedefi (mTOR) ve SIRT-1 immünoreaktivite yoğunluğu immünohistokimya ile değerlendirildi.
Bulgular: MTX grubunda testis seminifer tübülünde analizlenen Johnsen testis biyopsisi skoru kontrol grubuna kıyasla istatistiksel anlamda azalış gösterdi (p<0,001). Ovaryumda ise MTX tedavisi kontrol grubuna nazaran gözle görülür bir hasar meydana getirdi. Bu grupta foliküler dejenerasyon (p<0,05), damar konjesyonu (p<0,01) ve fibrozis (p<0,001) belirlendi. Hem testis hem de ovaryumda SCF immünoreaktivite yoğunluğu MTX grubunda azalma gösterdi (p<0,05). Ayrıca otofaji ile ilişkili belirteçlerden mTOR kontrol grubuna nazaran MTX gruplarında testis (p<0,05) ve ovaryumda (p<0,001) anlamlı bir şekilde azaldı. SIRT-1 yoğunluğu ise mTOR belirtecinin aksine hasar grubuda testis (p<0,001) ve ovaryumda (p<0,01) anlamlı bir artış gösterdi.
Sonuçlar: Sonuç olarak, araştırmamızda MTX’in testis ve yumurtalık üzerindeki olası olumsuz etkilerini değerlendirmek adına histopatolojik ve immünohistokimyasal analizler gerçekleştirdik. Ve analizlerimiz MTX tedavisinin gonadlar üzerinde kayda değer bir hasar oluşturduğunu bize gösterdi. Testis ve yumurtalık üzerindeki bu hasarın azaltılması veya tamamen ortadan kaldırılması adına antioksidan içeriklerinin kullanımı oldukça önemli bir alternatif olacaktır.
Keywords: Methotrexate; chemotherapy; ovary; testis.
Copyright© 2024 The Author. Published by Galenos Publishing House on behalf of Istanbul Medeniyet University Faculty of Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The protective effects of alpha lipoic acid on methotrexate induced testis injury in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:1486-1492. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.078. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29793311
-
Protective effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate against methotrexate-induced testicular damage.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021 Dec;40(12_suppl):S164-S177. doi: 10.1177/09603271211035674. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34340576
-
Effects of resveratrol on methotrexate-induced testicular damage in rats.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Jul 28;2013:489659. doi: 10.1155/2013/489659. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 23983634 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorating effects of agomelatine on testicular and epididymal damage induced by methotrexate in rats.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020 Mar;34(3):e22445. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22445. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31975554
-
Protective effects of curcumin against methotrexate-induced testicular damage in rats by suppression of the p38-MAPK and nuclear factor-kappa B pathways.Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2021 Sep;48(3):211-220. doi: 10.5653/cerm.2020.04105. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2021. PMID: 34352168 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cardioprotective effects of carvacrol in the isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction model.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Jul 14;26(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00967-3. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40660388 Free PMC article.
-
Royal jelly alleviates gemcitabine-induced ovarian toxicity: an investigation on rat models.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jul 14;25(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-05013-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40660206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kızıl HE, Caglayan C, Darendelioğlu E, et al. Morin ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity via targeting Nrf2/HO-1 and Bax/Bcl2/Caspase-3 signaling pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50:3479–88. - PubMed
-
- Varışlı B, Caglayan C, Kandemir FM, Gür C, Bayav İ, Genç A. The impact of Nrf2/HO-1, caspase-3/Bax/Bcl2 and ATF6/IRE1/PERK/GRP78 signaling pathways in the ameliorative effects of morin against methotrexate-induced testicular toxicity in rats. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49:9641–9. - PubMed
-
- Gunyeli I, Saygin M, Ozmen O. Methotrexate-induced toxic effects and the ameliorating effects of astaxanthin on genitourinary tissues in a female rat model. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2021;304:985–97. - PubMed
-
- Wei T, Wang L, Tang J, Ashaolu TJ, Olatunji OJ. Protective effect of Juglanin against doxorubicin-induced cognitive impairment in rats: Effect on oxidative, inflammatory and apoptotic machineries. Metab Brain Dis. 2022;37:1185–95. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
