Prognostic significance of blood immune cells in children with sepsis and establishment of a predictive model for PICU mortality: a retrospective study
- PMID: 39726536
- PMCID: PMC11669697
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1455216
Prognostic significance of blood immune cells in children with sepsis and establishment of a predictive model for PICU mortality: a retrospective study
Abstract
Objectives: This article aimed to investigate the correlation between blood immune cells and the prognosis in the early phase of pediatric sepsis and construct a prediction model for pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) mortality.
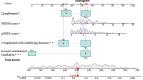
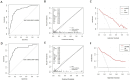
Methods: A total of 348 children admitted with sepsis to our PICU were retrospectively collected between January 2020 and June 2024. Of these, 242 children admitted from January 2020 to October 2022 were designated as the modeling group, while 106 children admitted between November 2022 and June 2024 were designated as the prospective validation group. Peripheral blood immune-related parameters, measured from the day of PICU admission to day 7, were analyzed in the modeling group. Risk factors were identified through multivariate logistic regression and integrated into a predictive nomogram. The nomogram was then applied to the prospective validation group to assess its discrimination and calibration. The nomogram's performance was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC), calibration plots, and decision curve analysis for both groups.
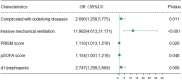
Results: Complicated with underlying diseases, invasive mechanical ventilation, increased pediatric risk of mortality score or pediatric sequential organ failure assessment score, and lymphopenia (d1) were independent risk factors for PICU mortality. The 90-day survival of patients with lymphopenia on the first day after admission was low. In addition, patients with persistent lymphopenia had higher mortality. The nomogram showed an AUC of 0.861 (95% CI: 0.813 to 0.909) in the modeling group and 0.875 (95% CI: 0.797 to 0.953) in the prospective validation group. The nomogram also performed well based on the calibration curve and decision curve analysis.
Conclusion: Assessing lymphocytes within seven days of PICU admission may be conducive to identifying children with sepsis at increased mortality risk. The nomogram performed well in predicting PICU mortality among patients of interest.
Keywords: PICU mortality; children; lymphocytes; predictive model; sepsis.
© 2024 He, Meng, Wei and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- James SL, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1789–858. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

