Bibliometric analysis and visualization of the research on the relationship between RNA methylation and immune cell infiltration in tumors
- PMID: 39726589
- PMCID: PMC11669668
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1477828
Bibliometric analysis and visualization of the research on the relationship between RNA methylation and immune cell infiltration in tumors
Abstract
Background: This research endeavors to delve into the research hotspots and trends concerning RNA methylation and tumor immune cells through the application of bibliometric analysis and visualization techniques.
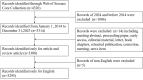
Methods: A comprehensive search in WoSCC (2014-2023) for RNA methylation and tumor immune cell articles/reviews was conducted. Bibliometric analysis and visualization employed CiteSpace, Bibliometric, and VOSviewer tools.
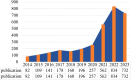
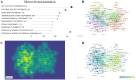
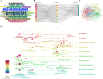
Results: A total of 3295 articles were included in the analysis, with a continuously increasing number of publications linking RNA methylation to tumoral immune cells. Chinese authors and research institutions have demonstrated a sustained growth trend in both the number of publications and author influence. SUN YAT SEN UNIVERSITY, a Chinese institution, has published the highest number of articles in this field, while also demonstrating extensive international and inter-institutional collaborations. Meanwhile, HARVARD UNIVERSITY has also achieved impressive results. For instance, Frontiers in Immunology has published the largest number of articles in this category. Nature Communications has published articles that are most influential in this field, playing a pivotal role in disseminating research findings. The sustained vitality of this field is attributed to its solid research foundation, including the groundbreaking work published by Professor Chiappinelli KB in Cell and the widely cited paper by Professor Han DL in Nature. Analysis of research trend topics reveals that m5C, immunotherapy, and the immune microenvironment are current research focuses.
Conclusion: Future investigative efforts at the juncture of RNA methylation and tumor immune cells are anticipated to concentrate on domains including m5C, n7-methylguanosine, cuproptosis, prognosis assessment, immunotherapeutic strategies, and the tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: RNA methylation; bibliometric analysis; immune cell; trend topics; web of science.
Copyright © 2024 Meng, Yang, Yu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Current perspectives and trends of CD39-CD73-eAdo/A2aR research in tumor microenvironment: a bibliometric analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1427380. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427380. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39188712 Free PMC article.
-
Liver cancer from the perspective of single-cell sequencing: a review combined with bibliometric analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 24;150(6):316. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05855-7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38910204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of mitochondrial damage on tumor microenvironment and immune response: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1442027. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1442027. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39104527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global research trends and focus on the link between neutrophil extracellular traps and tumor: a bibliometric and visualization analysis from 2006 to 2024.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 24;15:1452104. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1452104. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39381001 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging trends and research foci of oncolytic virotherapy for central nervous system tumors: A bibliometric study.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 6;13:975695. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.975695. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36148235 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

