Current research trends and hotspots of boron neutron capture therapy: a bibliometric and visualization analysis
- PMID: 39726703
- PMCID: PMC11669655
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1507157
Current research trends and hotspots of boron neutron capture therapy: a bibliometric and visualization analysis
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to describe the trends, current hotspots, and future directions in boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) through a bibliometric analysis.
Methods: Articles related to BNCT published before 2023-12-31 were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection database. VOSviewer, R, and CiteSpace were used for bibliometric analysis and visualization.
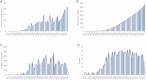
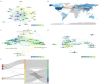
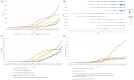
Results: A total of 3347 related publications from 1975 to 2023 were retrieved. Since a burst of published documents in 1992, the past three decades have witnessed continuous investigations into BNCT-related studies. Japan was the most productive country (794, 23.72%), followed by the USA (792, 23.66%), while the latter had the most citations. Kyoto University was the most influential institution. Ono K was the most prolific author, and Applied Radiation and Isotopes was the most popular journal. Ono K was the author that had the most total citations, followed by Barth RF. "Carborane", "boronophenylalanine", "glioblastoma", "sodium borocaptate", "cancer" and "drug delivery" were the most frequent keywords. The article "Dendrimers and dendritic polymers in drug delivery" had the most citations, whereas "Boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy of cancer" had the highest outbreak value.
Conclusion: Over the past three decades, research on BNCT has expanded significantly, with the development of novel boron carriers with improved medicinal characteristics being the most extensively investigated area. Future research will likely focus on the validation and modification of current BNCT treatment modalities using conventional boron agents in brain tumors, accelerator-based neutron sources and the application of BNCT in more clinical scenarios.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewer; bibliometric analysis; boron neutron capture therapy; research trends.
Copyright © 2024 Cong, Abulimiti, Matsumoto and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Global trends in research of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a bibliometric and visualization analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 2;14:1392245. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1392245. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39015496 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy for malignant glioma: a pilot neutron irradiation study using boron phenylalanine, sodium borocaptate and liposomal borocaptate with a heterotopic U87 glioblastoma model in SCID mice.Int J Radiat Biol. 2020 Jul;96(7):868-878. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1761039. Epub 2020 May 12. Int J Radiat Biol. 2020. PMID: 32339057
-
Evaluation of sodium borocaptate (BSH) and boronophenylalanine (BPA) as boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy (NCT) of cancer: an update and a guide for the future clinical evaluation of new boron delivery agents for NCT.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2024 Aug;44(8):893-909. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12582. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38973634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: current status and future prospects.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Jun 1;11(11):3987-4002. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0035. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15930333 Review.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

