Label-Free Metabolic Imaging In Vivo by Two-Photon Fluorescence Lifetime Endomicroscopy
- PMID: 39726730
- PMCID: PMC11671153
- DOI: 10.1021/acsphotonics.2c01493
Label-Free Metabolic Imaging In Vivo by Two-Photon Fluorescence Lifetime Endomicroscopy
Abstract
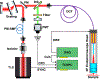
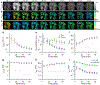
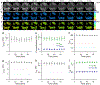
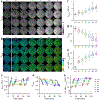
NADH intensity and fluorescence lifetime characteristics have proved valuable intrinsic biomarkers for profiling the cellular metabolic status of living biological tissues. To fully leverage the potential of NADH fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) in (pre)clinical studies and translational applications, a compact and flexible endomicroscopic embodiment is essential. Herein we present our newly developed two-photon fluorescence (2PF) lifetime imaging endomicroscope (2p-FLeM) that features an about 2 mm diameter, subcellular resolution, and excellent emission photon utilization efficiency and can extract NADH lifetime parameters of living tissues and organs reliably using a safe excitation power (~30 mW) and moderate pixel dwelling time (≤10 μs). In vivo experiments showed that the 2p-FLeM system was capable of tracking NADH lifetime dynamics of cultured cancer cells and subcutaneous mouse tumor models subject to induced apoptosis, and of a functioning mouse kidney undergoing acute ischemia-reperfusion perturbation. The complementary structural and metabolic information afforded by the 2p-FLeM system promises functional histological imaging of label-free internal organs in vivo and in situ for practical clinical diagnosis and therapeutics applications.
Keywords: NADH lifetime imaging; fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM); label-free imaging; metabolic imaging; two-photon endomicroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nelson DL; Cox MM; Lehninger AL Lehninger principles of biochemistry; W.H. Freeman, 2013.
-
- Vishwasrao HD; Heikal AA; Kasischke KA; Webb WW Conformational dependence of intracellular NADH on metabolic state revealed by associated fluorescence anisotropy. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 25119–25126. - PubMed
-
- Blinova K; Carroll S; Bose S; Smirnov AV; Harvey JJ; Knutson JR; Balaban RS Distribution of mitochondrial NADH fluorescence lifetimes: steady-state kinetics of matrix NADH interactions. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 2585–2594. - PubMed
-
- Bird DK; Yan L; Vrotsos KM; Eliceiri KW; Vaughan EM; Keely PJ; White JG; Ramanujam N Metabolic mapping of MCF10A human breast cells via multiphoton fluorescence lifetime imaging of the coenzyme NADH. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 8766–8773. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
