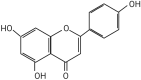
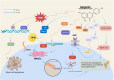
Pharmacology and mechanisms of apigenin in preventing osteoporosis
- PMID: 39726788
- PMCID: PMC11669520
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1486646
Pharmacology and mechanisms of apigenin in preventing osteoporosis
Abstract
Osteoporosis (OP) stands as the most prevalent systemic skeletal condition associated with aging. The current clinical management of OP predominantly depends on anti-resorptive and anabolic agents. Nevertheless, prolonged use of some of these medications has been observed to reduce efficacy and elevate adverse effects. Given the necessity for sustained or even lifelong treatment of OP, the identification of drugs that are not only effective but also safe and cost-efficient is of utmost significance. As disease treatment paradigms continue to evolve and recent advancements in OP research come to light, certain plant-derived compounds have emerged, presenting notable benefits in the management of OP. This review primarily explores the pharmacological properties of apigenin and elucidates its therapeutic mechanisms in the context of OP. The insights provided herein aspire to offer a foundation for the judicious use of apigenin in forthcoming research, particularly within the scope of OP.
Keywords: apigenin; inflammatory factors; osteoblasts; osteoporosis; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2024 Lin, Yincang, Jiazhe, Xilin and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aibar-Almazán A., Voltes-Martínez A., Castellote-Caballero Y., Afanador- Restrepo D. F., Carcelén-Fraile M. D. C., López-Ruiz E. (2022). Current status of the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis management of osteoporosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23(16):9465. 10.3390/ijms23169465 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alfaleh M. A., Hashem A. M., Abujamel T. S., Alhakamy N. A., Kalam M. A., Riadi Y., et al. (2022). Apigenin loaded lipoid-PLGA-TPGS nanoparticles for colon cancer therapy: characterization, sustained release, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis pathways for colon cancer therapy: characterization, sustained release, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis pathways. Polymers 14(17), 3577. 10.3390/polym14173577 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- An X., Shang F. (2018). RA-XII exerts anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute renal injury by suppressing NF-κB and MAPKs regulated by HO-1/Nrf2 pathway activities on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute renal injury by suppressing NF- κ B and MAPKs regulated by HO-1/Nrf2 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 495 (3), 2317–2323. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.131 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous