Effectiveness of switching strategies in CGRP monoclonal antibody therapy for migraine: A retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 39727075
- PMCID: PMC11951397
- DOI: 10.1111/head.14865
Effectiveness of switching strategies in CGRP monoclonal antibody therapy for migraine: A retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of first switching between monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) or its receptor in the treatment of migraine.
Background: Although mAbs targeting CGRP or its receptor have emerged as a leading treatment for migraine prevention, a proportion of patients do not respond. While switching between these antibodies is a common clinical practice in such cases, the effectiveness remains a subject of study.
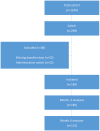
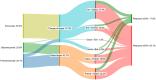
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study at a tertiary headache center, analyzing data from clinical records of patients treated with anti-CGRP mAbs from January 2020 to March 2024. Baseline was defined as the monthly headache days (MHDs) in the 3 months prior to the start of the second mAb. The primary endpoint was the change in MHDs at month 3 and month 6 following the switch. Additionally, we evaluated response rates in both periods. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on changes in mechanism of action. Finally, we assessed the influence of the number of doses of the first mAb and the inter-treatment interval.
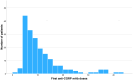
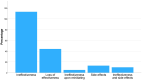
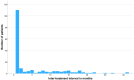
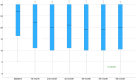
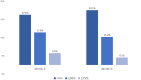
Results: Out of 1244 initially identified patients, 185 were included in the month-3 analysis and 123 in the month-6 evaluation. The median MHDs decreased from 27.0 (interquartile range [IQR] 16.1, 30.0; range 5.0, 30.7) at baseline to 21.0 (IQR 10.0, 30.0; range 0.0, 30.0; p < 0.001) at month 3, and to 20.0 (IQR 10.0, 30.0; range 0.0, 31.0; p < 0.001) at month 6. Subgroup analyses revealed no significant differences in MHDs between maintaining the same target or changing it (baseline: 28.0 [IQR 16.2, 30.0; range 5.0, 31.0] vs. 27.0 [IQR 6.0, 31.0; range 6.0, 31.0]; month 3: 23.0 [IQR 10.0, 30.0; range 0.0, 31.0] vs. 19.0 [IQR 11.0, 30.0; range 1.0, 31.0], p = 0.144; month 6: 24.0 [IQR 11.0, 30.0; range 0.0, 31.0] vs. 17.0 [IQR 10.0, 30.0; range 3.0, 31.0], p = 0.170). There was no association between a ≥50% reduction in MHDs and the number of previous doses of the first mAb (odds ratio [OR] 1.0; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.0, 1.1; p = 0.189) or the inter-treatment interval (OR 1.0; 95% CI 0.9, 1.1; p = 0.914).
Conclusion: Switching between anti-CGRP mAbs resulted in a reduction in MHDs, with no significant differences based on the mechanism of action. Factors such as the number of doses of the first mAb and the inter-treatment interval did not appear to predict a ≥50% reduction in MHDs at month 3. Our findings support the viability of switching as an effective treatment option for patients with migraine who do not respond to initial mAb therapy.
Keywords: calcitonin gene–related peptide; headache; migraine; monoclonal antibody; switch.
© 2024 The Author(s). Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Headache Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Persistence, effectiveness, and tolerability of anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies in patients with chronic migraine.Headache. 2025 Jan;65(1):24-34. doi: 10.1111/head.14827. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Headache. 2025. PMID: 39268992
-
Retrospective cohort study of anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody unresponsive migraine individuals treated with atogepant: The RESCUE study.Cephalalgia. 2025 Jun;45(6):3331024251346925. doi: 10.1177/03331024251346925. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Cephalalgia. 2025. PMID: 40501126
-
Monoclonal antibodies targeting the calcitonin gene-related peptide pathway improve the effectiveness of acute medication-a real-world study.Neurol Sci. 2024 Jul;45(7):3305-3312. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07380-4. Epub 2024 Feb 10. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38340218 Free PMC article.
-
Indirect Comparison of Topiramate and Monoclonal Antibodies Against CGRP or Its Receptor for the Prophylaxis of Episodic Migraine: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.CNS Drugs. 2021 Aug;35(8):805-820. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00834-9. Epub 2021 Jul 16. CNS Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34272688 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological differences and switching among anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies: A narrative review.Headache. 2025 Feb;65(2):342-352. doi: 10.1111/head.14903. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Headache. 2025. PMID: 39825578 Review.
References
-
- Skljarevski V, Matharu M, Millen BA, Ossipov MH, Kim BK, Yang JY. Efficacy and safety of galcanezumab for the prevention of episodic migraine: results of the EVOLVE‐2 phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trial. Cephalalgia. 2018;38(8):1442‐1454. - PubMed
-
- Dodick DW, Ashina M, Brandes JL, et al. ARISE: a phase 3 randomized trial of erenumab for episodic migraine. Cephalalgia. 2018;38(6):1026‐1037. - PubMed
-
- Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, Hallström Y, et al. A controlled trial of Erenumab for episodic migraine. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(22):2123‐2132. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

