The ATPase activity of yeast chromosome axis protein Hop1 affects the frequency of meiotic crossovers
- PMID: 39727188
- PMCID: PMC11797056
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1264
The ATPase activity of yeast chromosome axis protein Hop1 affects the frequency of meiotic crossovers
Abstract
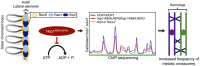
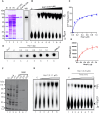
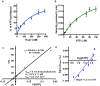
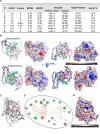
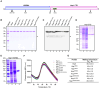
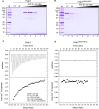
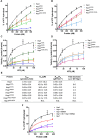
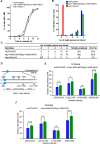
Saccharomyces cerevisiae meiosis-specific Hop1, a structural constituent of the synaptonemal complex, also facilitates the formation of programmed DNA double-strand breaks and the pairing of homologous chromosomes. Here, we reveal a serendipitous discovery that Hop1 possesses robust DNA-independent ATPase activity, although it lacks recognizable sequence motifs required for ATP binding and hydrolysis. By leveraging molecular docking combined with molecular dynamics simulations and biochemical assays, we identified an ensemble of five amino acid residues in Hop1 that could potentially participate in ATP-binding and hydrolysis. Consistent with this premise, we found that Hop1 binds to ATP and that substitution of amino acid residues in the putative ATP-binding site significantly impaired its ATPase activity, suggesting that this activity is intrinsic to Hop1. Notably, K65A and N67Q substitutions in the Hop1 N-terminal HORMA domain synergistically abolished its ATPase activity, noticeably impaired its DNA-binding affinity and reduced its association with meiotic chromosomes, while enhancing the frequency of meiotic crossovers (COs). Overall, our study establishes Hop1 as a DNA-independent ATPase and reveals a potential biological function for its ATPase activity in the regulation of meiotic CO frequency.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pch2 is a hexameric ring ATPase that remodels the chromosome axis protein Hop1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 7;111(1):E44-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310755111. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24367111 Free PMC article.
-
Pch2 acts through Xrs2 and Tel1/ATM to modulate interhomolog bias and checkpoint function during meiosis.PLoS Genet. 2011 Nov;7(11):e1002351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002351. Epub 2011 Nov 3. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22072981 Free PMC article.
-
The Pch2 AAA+ ATPase promotes phosphorylation of the Hop1 meiotic checkpoint adaptor in response to synaptonemal complex defects.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 19;44(16):7722-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw506. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27257060 Free PMC article.
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hop1 zinc finger motif is the minimal region required for its function in vitro.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 9;279(28):28961-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403727200. Epub 2004 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15123624
-
Turning coldspots into hotspots: targeted recruitment of axis protein Hop1 stimulates meiotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2022 Aug 30;222(1):iyac106. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac106. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35876814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Page S.L., Hawley R.S.. The genetics and molecular biology of the synaptonemal complex. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004; 20:525–558. - PubMed
-
- Cahoon C.K., Hawley R.S.. Regulating the construction and demolition of the synaptonemal complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016; 23:369–377. - PubMed
-
- Ur S.N., Corbett K.D.. Architecture and dynamics of meiotic chromosomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2021; 55:497–526. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

