Autophosphorylation of the Tousled-like kinases TLK1 and TLK2 regulates recruitment to damaged chromatin via PCNA interaction
- PMID: 39727191
- PMCID: PMC11879137
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1279
Autophosphorylation of the Tousled-like kinases TLK1 and TLK2 regulates recruitment to damaged chromatin via PCNA interaction
Abstract
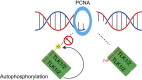
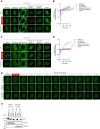
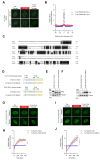
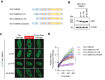
Tousled-like kinases 1 and 2 (TLK1 and 2) are cell cycle-regulated serine/threonine kinases that are involved in multiple biological processes. Mutation of TLK1 and 2 confer neurodegenerative diseases. Recent studies demonstrate that TLK1 and 2 are involved in DNA repair. However, there is no direct evidence that TLK1 and 2 function at DNA damage sites. Here, we show that both TLK1 and TLK2 are hyper-autophosphorylated at their N-termini, at least in part, mediated by their homo- or hetero- dimerization. We found that TLK1 and 2 hyper-autophosphorylation suppresses their recruitment to damaged chromatin. Furthermore, both TLK1 and 2 associate with PCNA specifically through their evolutionarily conserved non-canonical PCNA-interacting protein (PIP) box at the N-terminus, and mutation of the PIP-box abolishes their recruitment to DNA damage sites. Mechanistically, the TLK1 and 2 hyper-autophosphorylation masks the PIP-box and negatively regulates their recruitment to the DNA damage site. Overall, our study dissects the detailed genetic regulation of TLK1 and 2 at damaged chromatin, which provides important insights into their emerging roles in DNA repair.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Update of
-
Autophosphorylation of the Tousled-like kinases TLK1 and TLK2 regulates recruitment to damaged chromatin via PCNA interaction.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 26:2024.04.22.590659. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.22.590659. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 08;53(4):gkae1279. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1279. PMID: 38712247 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Autophosphorylation of the Tousled-like kinases TLK1 and TLK2 regulates recruitment to damaged chromatin via PCNA interaction.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 26:2024.04.22.590659. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.22.590659. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 08;53(4):gkae1279. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1279. PMID: 38712247 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Structural Basis for the Interaction Between Yeast Chromatin Assembly Factor 1 and Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen.J Mol Biol. 2024 Aug 15;436(16):168695. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168695. Epub 2024 Jul 4. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38969056 Free PMC article.
-
Srs2 binding to proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and its sumoylation contribute to replication protein A (RPA) antagonism during the DNA damage response.Elife. 2025 Aug 1;13:RP98843. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98843. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40748045 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing weight gain after smoking cessation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD006219. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006219.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 6;10:CD006219. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006219.pub4. PMID: 22258966 Updated.
-
Thrombopoietin receptor agonists for prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with solid tumours.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 27;11(11):CD012035. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012035.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29178132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shalom S., Don J. Tlk, a novel evolutionarily conserved murine serine threonine kinase, encodes multiple testis transcripts. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1999; 52:392–405. - PubMed
-
- Roe J.L., Rivin C.J., Sessions R.A., Feldmann K.A., Zambryski P.C. The Tousled gene in A. thaliana encodes a protein kinase homolog that is required for leaf and flower development. Cell. 1993; 75:939–950. - PubMed
-
- Li Y., DeFatta R., Anthony C., Sunavala G., De Benedetti A. A translationally regulated Tousled kinase phosphorylates histone H3 and confers radioresistance when overexpressed. Oncogene. 2001; 20:726–738. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

