Annexin A1 Mitigates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in a Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy Model by Enhancing the Expression of Occludin and Zonula Occludens-1 (ZO-1)
- PMID: 39727329
- PMCID: PMC11672249
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.70173
Annexin A1 Mitigates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in a Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy Model by Enhancing the Expression of Occludin and Zonula Occludens-1 (ZO-1)
Abstract
Aims: This study investigated the protective role of Annexin A1 (ANXA1) in sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) by examining its effects on brain vascular endothelium and blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity.
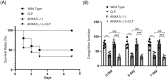
Methods: Mice were divided into four groups: wild type (WT), cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), ANXA1 knockout (ANXA1[-/-]), and ANXA1(-/-) with CLP. Neurobehavioral changes were assessed using the Y-maze test, while BBB integrity was evaluated through Evans blue dye (EBD) staining and permeability tests with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran.
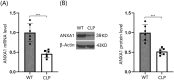
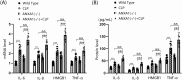
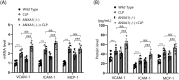
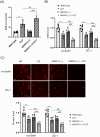
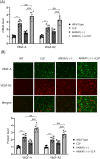
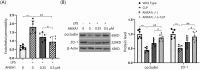
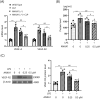
Results: Results showed that ANXA1 levels were reduced in septic mice, and its deficiency exacerbated cognitive impairment and survival rate reduction. ANXA1 deficiency also upregulated proinflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules, worsened BBB impairment, and altered expression of tight junction proteins and VEGF-A/VEGF-R2. In vitro, ANXA1 Ac2-26 prevented LPS-induced increased permeability in bEnd.3 cells by restoring tight junction proteins and reducing VEGF-A/VEGF-R2 expression. Notably, VEGF-A negated the protective effects of ANXA1 Ac2-26.
Conclusion: The study concludes that ANXA1 reduces BBB permeability to protect against sepsis-induced brain dysfunction via VEGF-A/VEGF-R2 regulation of tight junction proteins, suggesting ANXA1 as a potential therapeutic for SAE.
Keywords: VEGF; annexin A1; blood brain barrier; occludin; sepsis‐associated encephalopathy.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
orexin B alleviates sepsis-associated lung injury through the attenuation of pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction by regulating the rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2/zonula occludens-1 (ROCK2/ZO-1) axis.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2025 Aug;72(4):883-896. doi: 10.1002/bab.2703. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39623599
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture on expression in blood-brain barrier in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating HIF-1α/VEGF/MMP-9 signaling pathway].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 Jun 25;50(6):613-623. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20241047. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40551643 Chinese.
-
INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL-SPECIFIC OCCLUDIN DELETION WORSENS GUT PERMEABILITY AND SURVIVAL FOLLOWING SEPSIS.Shock. 2025 Apr 1;63(4):597-605. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002531. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Shock. 2025. PMID: 39637366
-
A Cell-Based Systematic Review on the Role of Annexin A1 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 26;23(15):8256. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158256. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897832 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanobiology of the blood-brain barrier during development, disease and ageing.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 6;16(1):7233. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61888-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40769996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut-Brain Axis-Based Polygala Tenuifolia and Magnolia Officinalis Improve D-gal-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Mice Through cAMP and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Mar 13;19:1869-1894. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S506545. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40098911 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuins in mitophagy: key gatekeepers of mitochondrial quality.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jul 24. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05358-0. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40705152 Review.
References
-
- Wang W. and Liu C. F., “Sepsis Heterogeneity,” World Journal of Pediatrics 19 (2023): 919–927. - PubMed
-
- Chiu C. and Legrand M., “Epidemiology of Sepsis and Septic Shock,” Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology 34 (2021): 71–76. - PubMed
-
- Tauber S. C., Djukic M., Gossner J., Eiffert H., Bruck W., and Nau R., “Sepsis‐Associated Encephalopathy and Septic Encephalitis: An Update,” Expert Review of Anti‐Infective Therapy 19 (2021): 215–231. - PubMed
-
- Hong Y., Chen P., Gao J., Lin Y., Chen L., and Shang X., “Sepsis‐Associated Encephalopathy: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Management,” International Immunopharmacology 124 (2023): 110800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

