Construction and characterization of bioluminescent Salmonella Reading outbreak and non-outbreak strains
- PMID: 39727399
- PMCID: PMC11792501
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01263-24
Construction and characterization of bioluminescent Salmonella Reading outbreak and non-outbreak strains
Abstract
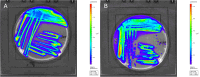
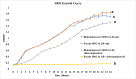
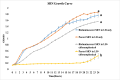
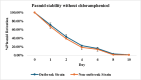
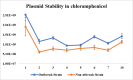
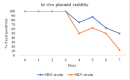
Salmonella enterica serotype Reading has recently been identified as a significant foodborne pathogen from contaminated poultry products. There is a critical need for close monitoring of this newly emerged pathogen. This study developed bioluminescent strains of S. Reading for real-time pathogen tracking using bioluminescence imaging. Two strains of S. Reading were used: an outbreak strain and a non-outbreak strain. The chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene was cloned into the plasmid pBS-slpGFPluxABCDE, which carries luxABCDE operon and an ampicillin resistance gene. The newly constructed plasmid was then transformed into the outbreak and non-outbreak strains of S. Reading by electroporation. The resulting colonies were confirmed by visualizing bioluminescence using an in vivo imaging system and by testing their resistance to chloramphenicol. These strains demonstrated a high bioluminescence level (108-109 Photons/s/cm2/sr) and were tested for growth and plasmid stability by daily subculturing in Luria-Bertani medium with and without antibiotics. The plasmid remained stable for 8 days under non-selective conditions, and growth rates were comparable to non-bioluminescent parent strains in antibiotic-free conditions. However, growth was notably different in the presence of chloramphenicol, indicating successful plasmid retention and function. This study successfully created stable bioluminescent S. Reading strains, marking a significant step forward in monitoring and potentially reducing the spread of this emergent foodborne pathogen in the poultry industry.
Importance: Salmonella enterica serotype Reading has recently become a significant foodborne pathogen linked to poultry products. To enhance pathogen monitoring, this study developed bioluminescent strains of S. Reading by inserting the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene into a plasmid containing a bioluminescence gene cluster. These modified strains were transformed into outbreak and non-outbreak bacterial strains via electroporation. The bioluminescent strains demonstrated stable plasmid retention and high bioluminescence levels. They also showed growth comparable to their parent strains, even in the absence of antibiotics. These bioluminescent strains could potentially facilitate real-time monitoring and control of S. Reading in poultry industries.
Keywords: Salmonella Reading; bioluminescence imaging; foodborne pathogen; outbreaks; transformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Research Note: Evaluating the vertical transmission potential of Salmonella Reading in broiler breeders.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104351. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104351. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39368433 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of a Novel Salmonella enterica Serotype Reading Clonal Group Is Linked to Its Expansion in Commercial Turkey Production, Resulting in Unanticipated Human Illness in North America.mSphere. 2020 Apr 15;5(2):e00056-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00056-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32295868 Free PMC article.
-
Fifteen years of successful spread of Salmonella enterica serovar Mbandaka clone ST413 in Poland and its public health consequences.Ann Agric Environ Med. 2016 Jun 2;23(2):237-41. doi: 10.5604/12321966.1203883. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2016. PMID: 27294625
-
Molecular characterisation of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Infantis from humans, animals and the environment in Italy.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011 Nov;38(5):384-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Aug 6. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011. PMID: 21821397
-
A Bright Future for Fluorescence Imaging of Fungi in Living Hosts.J Fungi (Basel). 2019 Apr 3;5(2):29. doi: 10.3390/jof5020029. J Fungi (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30987114 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wibisono FM, Wibison FJ, Effendi MH, Plumeriastuti H, Hidayatullah AR, Hartadi EB, Sofiana ED. 2020. A review of Salmonellosis on poultry farms: public health importance. Syst Rev Pharm 11:481–486. doi:10.31838/srp.2020.9.69 - DOI
-
- O’Bryan CA, Ricke SC, Marcy JA. 2022. Public health impact of Salmonella spp. on raw poultry: current concepts and future prospects in the United States. Food Control 132:108539. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108539 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

