Quantitative Assessment of Apically Extruded Debris During Retreatment Procedures Using Three Nickel-Titanium Rotary Systems: An In Vitro Comparative Study
- PMID: 39727441
- PMCID: PMC11674195
- DOI: 10.3390/dj12120384
Quantitative Assessment of Apically Extruded Debris During Retreatment Procedures Using Three Nickel-Titanium Rotary Systems: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Abstract
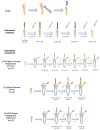
Objectives: Apical extrusion of debris can affect the success of endodontic treatments, and the specific performance of certain retreatment systems has not been studied yet. Therefore, the aim of this in vitro study was to quantitatively assess the amount of apically extruded debris produced during retreatment procedures using three rotary NiTi retreatment systems in mature non-resorbed straight roots. Methods: Thirty extracted permanent human teeth with single straight roots were selected. The root canals were prepared with the ProTaper Next system up to size 30 and obturated with gutta-percha and AH Plus sealer using the continuous wave of condensation technique. The samples were stored for 30 days and randomized by computer sequence into three retreatment groups (n = 10): (1) ProTaper Universal Retreatment; (2) HyFlex Remover; and (3) VDW.Rotate Retreatment. Apically extruded debris was collected in Eppendorf tubes and weighed with a microbalance (10-5 g) before and after retreatment procedure. As the data were not normally distributed, the Kruskal-Wallis test was applied for comparing data among groups, with an alpha level set at α = 0.05. Dunn's test was considered for post-hoc analyses, if appropriate. Results: Hyflex Remover was associated with the highest amount of extruded debris (0.85 ± 0.82 mg), followed by VDW.Rotate Retreatment (0.78 ± 0.41 mg) and ProTaper Universal Retreatment (0.62 ± 0.28 mg). However, the differences were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). Conclusions: All the retreatment systems tested were associated with apical extrusion of debris in vitro, with no significant quantitative differences between them, suggesting that clinicians can choose a retreatment system with features appropriate to the specific clinical situation without risk of increasing the amount of apically extruded debris.
Keywords: HyFlex Remover; ProTaper Retreatment; VDW.Rotate Retreatment; apically extruded debris; retreatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Apically Extruded Debris During Retreatment Procedures Using Various File Systems in Teeth With Simulated Apical Root Resorption: An In Vitro Study.Cureus. 2023 Jun 24;15(6):e40904. doi: 10.7759/cureus.40904. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37492825 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of apically extruded debris during the removal of canal filling material using three different Ni-Ti systems and hand files in teeth with simulated apical root resorption.Int Endod J. 2020 Mar;53(3):403-409. doi: 10.1111/iej.13234. Epub 2019 Nov 3. Int Endod J. 2020. PMID: 31605377
-
Evaluation of Apically Extruded Debris from Curved Root Canal Filling Removal Using 5 Nickel-Titanium Systems.J Endod. 2016 Jul;42(7):1101-4. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2016.03.012. Epub 2016 May 11. J Endod. 2016. PMID: 27179592
-
Efficiency and apical extrusion of debris: a comparative ex vivo study of four retreatment techniques in severely curved root canals.Int Endod J. 2017 Sep;50(9):910-918. doi: 10.1111/iej.12708. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Int Endod J. 2017. PMID: 27706822
-
Evaluation of debris extruded apically during the removal of root canal filling material using ProTaper, D-RaCe, and R-Endo rotary nickel-titanium retreatment instruments and hand files.J Endod. 2014 Dec;40(12):2066-9. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.09.004. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Endod. 2014. PMID: 25443282
References
-
- Hülsmann M., Drebenstedt S., Holscher C. Shaping and Filling Root Canals during Root Canal Re-treatment. Endod. Top. 2008;19:74–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-1546.2011.00264.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials