Tunable Alginate-Polyvinyl Alcohol Bioinks for 3D Printing in Cartilage Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 39727587
- PMCID: PMC11675395
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10120829
Tunable Alginate-Polyvinyl Alcohol Bioinks for 3D Printing in Cartilage Tissue Engineering
Abstract
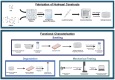
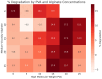
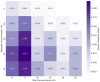
This study investigates 3D extrusion bioinks for cartilage tissue engineering by characterizing the physical properties of 3D-printed scaffolds containing varying alginate and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) concentrations. We systematically investigated the effects of increasing PVA and alginate concentrations on swelling, degradation, and the elastic modulus of printed hydrogels. Swelling decreased significantly with increased PVA concentrations, while degradation rates rose with higher PVA concentrations, underscoring the role of PVA in modulating hydrogel matrix stability. The highest elastic modulus value was achieved with a composite of 5% PVA and 20% alginate, reaching 0.22 MPa, which approaches that of native cartilage. These findings demonstrate that adjusting PVA and alginate concentrations enables the development of bioinks with tailored physical and mechanical properties, supporting their potential use in cartilage tissue engineering and other biomedical applications.
Keywords: 3D bioprinting; 3D scaffold; PVA; alginate; bioink; cartilage; hydrogel; matrix; polyvinyl alcohol; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Bioprinting Via a Dual-Gel Bioink Based on Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Solubilized Extracellular Matrix towards Cartilage Engineering.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 9;22(8):3901. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083901. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918892 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a novel alginate-polyvinyl alcohol-hydroxyapatite hydrogel for 3D bioprinting bone tissue engineered scaffolds.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017 May;105(5):1457-1468. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36036. Epub 2017 Feb 25. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017. PMID: 28187519
-
3D Printed Chitosan Composite Scaffold for Chondrocytes Differentiation.Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(7):832-842. doi: 10.2174/1573405616666201217112939. Curr Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33334294
-
Advanced Strategies for 3D Bioprinting of Tissue and Organ Analogs Using Alginate Hydrogel Bioinks.Mar Drugs. 2021 Dec 15;19(12):708. doi: 10.3390/md19120708. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34940707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing bioinks for 3D bioprinting using reactive fillers: A review.Acta Biomater. 2020 Sep 1;113:1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.06.040. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32622053 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibacterial Crosslinker for Ternary PCL-Reinforced Hydrogels Based on Chitosan, Polyvinyl Alcohol, and Gelatin for Tissue Engineering.Polymers (Basel). 2025 May 29;17(11):1520. doi: 10.3390/polym17111520. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508766 Free PMC article.
-
Designing Multifunctional Microneedles in Biomedical Engineering: Materials, Methods, and Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 4;20:8693-8728. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S531898. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40630938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asy-Syifa N., Kusjuriansah, Waresindo W.X., Edikresnha D., Suciati T., Khairurrijal K. The Study of the Swelling Degree of the PVA Hydrogel with Varying Concentrations of PVA. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022;2243:012053. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2243/1/012053. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

