Differentiating Benign from Malignant Causes of Splenomegaly: Is Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography Helpful?
- PMID: 39727638
- PMCID: PMC11727207
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases12120308
Differentiating Benign from Malignant Causes of Splenomegaly: Is Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography Helpful?
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the ability of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography in differentiating benign from malignant etiologies of splenomegaly based on differences in splenic stiffness.
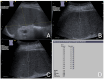
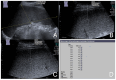
Materials and methods: Between September 2020 and November 2022, we evaluated 40 patients with splenomegaly-defined by a splenic long axis greater than 13 cm and/or a short axis greater than 6 cm, without visible focal or infiltrative mass lesions-using abdominal ultrasound at our university hospital. Each patient also underwent a standardized ARFI elastographic assessment of the enlarged spleen, with data collected prospectively. We then retrospectively analyzed the cases with confirmed etiologies of splenomegaly from their final medical reports. Mean ARFI velocities (MAV) were compared across patients with splenomegaly due to malignant infiltration (MIS) from hematological malignancy, congestive splenomegaly (CS) due to portal or splenic vein congestion/occlusion, and immune-related splenomegaly (IRS) associated with systemic infectious or autoimmune diseases.
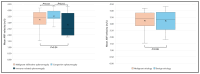
Results: Among the 40 patients with splenomegaly, 21 (52.5%) were diagnosed with malignant infiltrative splenomegaly (MIS), 11 (27.5%) with congestive splenomegaly (CS), and 8 (20%) with immune-related splenomegaly (IRS). The mean ARFI velocities (MAV) for the MIS, CS, and IRS groups were 3.25 ± 0.68 m/s, 3.52 ± 0.47 m/s, and 2.84 ± 0.92 m/s, respectively. No significant differences were observed in splenic stiffness (MAV) among these groups.
Conclusions: Differentiating between benign and malignant etiologies of splenomegaly based on stiffness differences observed in ARFI elastography is not feasible. Larger prospective studies are necessary to validate these findings.
Keywords: ARFI; point shear wave elastography; spleen; splenomegaly; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) Elastography of Focal Splenic Lesions: Feasibility and Diagnostic Potential.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;15(20):4964. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204964. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894331 Free PMC article.
-
Spleen stiffness measurement by shear wave elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse in predicting the etiology of splenomegaly.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Feb;46(2):609-615. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02649-6. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 32770399
-
Role of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography in the Characterization of Focal Solid Hepatic Lesions.J Clin Imaging Sci. 2018 Feb 21;8:5. doi: 10.4103/jcis.JCIS_64_17. eCollection 2018. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2018. PMID: 29541491 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Shear Wave Velocity Measurement on Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Differential Diagnosis between Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: A Meta-analysis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015 Dec;41(12):3035-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Sep 12. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26371402 Review.
-
Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for differentiation of malignant and benign breast lesions: a meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):4753-61. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stevens W.J., Bortier H., Van Meir F. Anatomy, Embryology, Histology and Physiology of the Spleen. In: De Schepper A.M., Vanhoenacker F., editors. Medical Imaging of the Spleen. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2000. pp. 1–6.
-
- Chapman J., Goyal A., Azevedo A.M. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Splenomegaly.
-
- Aldulaimi S., Mendez A.M. Splenomegaly: Diagnosis and Management in Adults. Am. Fam. Physician. 2021;104:271–276. - PubMed
-
- Justiz Vaillant A.A., Goyal A., Varacallo M. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

