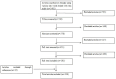
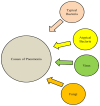
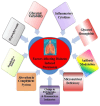
A Review on Risk Factors, Traditional Diagnostic Techniques, and Biomarkers for Pneumonia Prognostication and Management in Diabetic Patients
- PMID: 39727640
- PMCID: PMC11726889
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases12120310
A Review on Risk Factors, Traditional Diagnostic Techniques, and Biomarkers for Pneumonia Prognostication and Management in Diabetic Patients
Abstract
People of all ages can contract pneumonia, and it can cause mild to severe disease and even death. In addition to being a major cause of death for elderly people and those with prior medical conditions such as diabetes, it isthe world's biggest infectious cause of death for children. Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic condition with a high glucose level and is a leading cause of lower limb amputation, heart attacks, strokes, blindness, and renal failure. Hyperglycemia is known to impair neutrophil activity, damage antioxidant status, and weaken the humoral immune system. Therefore, diabetic patients are more susceptible to pneumonia than people without diabetes and linked fatalities. The absence of quick, precise, simple, and affordable ways to identify the etiologic agents of community-acquired pneumonia has made diagnostic studies' usefulness contentious. Improvements in biological markers and molecular testing techniques have significantly increased the ability to diagnose pneumonia and other related respiratory infections. Identifying the risk factors for developing severe pneumonia and early testing in diabetic patients might lead to a significant decrease in the mortality of diabetic patients with pneumonia. In this regard, various risk factors, traditional testing techniques, and pathomechanisms are discussed in this review. Further, biomarkers and next-generation sequencing are briefly summarized. Finding biomarkers with the ability to distinguish between bacterial and viral pneumonia could be crucial because identifying the precise pathogen would stop the unnecessary use of antibiotics and effectively save the patient's life.
Keywords: biomarkers; diabetes mellitus; diabetes-induced pneumonia; risk factors; traditional diagnostic techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Antar S.A., Ashour N.A., Sharaky M., Khattab M., Ashour N.A., Zaid R.T., Roh E.J., Elkamhawy A., Al-Karmalawy A.A. Diabetes mellitus: Classification, mediators, and complications; A gate to identify potential targets for the development of new effective treatments. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023;168:115734. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115734. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources