Edge Artificial Intelligence Device in Real-Time Endoscopy for Classification of Gastric Neoplasms: Development and Validation Study
- PMID: 39727787
- PMCID: PMC11672907
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics9120783
Edge Artificial Intelligence Device in Real-Time Endoscopy for Classification of Gastric Neoplasms: Development and Validation Study
Abstract
Objective: We previously developed artificial intelligence (AI) diagnosis algorithms for predicting the six classes of stomach lesions. However, this required significant computational resources. The incorporation of AI into medical devices has evolved from centralized models to decentralized edge computing devices. In this study, a deep learning endoscopic image classification model was created to automatically categorize all phases of gastric carcinogenesis using an edge computing device.
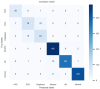
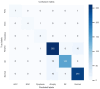
Design: A total of 15,910 endoscopic images were collected retrospectively and randomly assigned to train, validation, and internal-test datasets in an 8:1:1 ratio. The major outcomes were as follows: 1. lesion classification accuracy in six categories: normal/atrophy/intestinal metaplasia/dysplasia/early/advanced gastric cancer; and 2. the prospective evaluation of classification accuracy in real-world procedures.
Results: The internal-test lesion-classification accuracy was 93.8% (95% confidence interval: 93.4-94.2%); precision was 88.6%, recall was 88.3%, and F1 score was 88.4%. For the prospective performance test, the established model attained an accuracy of 93.3% (91.5-95.1%). The established model's lesion classification inference speed was 2-3 ms on GPU and 5-6 ms on CPU. The expert endoscopists reported no delays in lesion classification or any interference from the deep learning model throughout their exams.
Conclusions: We established a deep learning endoscopic image classification model to automatically classify all stages of gastric carcinogenesis using an edge computing device.
Keywords: deep learning; edge computing; endoscopy; gastric neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Decision Support System for All Stages of Gastric Carcinogenesis in Real-Time Endoscopy: Model Establishment and Validation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Oct 30;25:e50448. doi: 10.2196/50448. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37902818 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-aided diagnosis in real-time endoscopy for all stages of gastric carcinogenesis: Development and validation study.United European Gastroenterol J. 2024 May;12(4):487-495. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12551. Epub 2024 Feb 24. United European Gastroenterol J. 2024. PMID: 38400815 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based clinical decision support system for gastric neoplasms in real-time endoscopy: development and validation study.Endoscopy. 2023 Aug;55(8):701-708. doi: 10.1055/a-2031-0691. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Endoscopy. 2023. PMID: 36754065 Clinical Trial.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.Dig Dis. 2022;40(4):395-408. doi: 10.1159/000518232. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Dig Dis. 2022. PMID: 34348267 Review.
-
Accuracy of artificial intelligence-assisted endoscopy in the diagnosis of gastric intestinal metaplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 May 14;19(5):e0303421. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303421. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38743709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim I.-H., Kang S.J., Choi M., Kim B.-H., Eom B.W., Kim B.J., Min B.-H., Choi C.I., Shin C.M., Tae C.H., et al. Korean Practice Guidelines for Gastric Cancer 2022: An Evidence-based, Multidisciplinary Approach. J. Gastric Cancer. 2023;23:3–106. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2023.23.e11. Corrected in J. Gastric Cancer 2023, 23, 365. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gong E.J., Bang C.S., Lee J.J., Jeong H.M., Baik G.H., Jeong J.H., Dick S., Lee G.H. Clinical Decision Support System for All Stages of Gastric Carcinogenesis in Real-Time En-doscopy: Model Establishment and Validation Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023;25:e50448. doi: 10.2196/50448. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee J.W., Woo D., Kim K.O., Kim S.K., Lee H.S., Kang B., Lee Y.J., Kim J., Jang B.I., Kim E.Y., et al. Deep Learning Model Using Stool Pictures for Predicting Endoscopic Mucosal Inflammation in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024 doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002978. online ahead of print . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources