Impedimetric Sensor for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Detection: Performance Assessment with an ACE2 Peptide-Mimic/Graphite Interface
- PMID: 39727857
- PMCID: PMC11674363
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14120592
Impedimetric Sensor for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Detection: Performance Assessment with an ACE2 Peptide-Mimic/Graphite Interface
Abstract
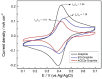
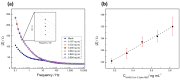
The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted the need for the development of new biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Particularly, systems with qualities such as sensitivity, fast detection, appropriate to large-scale analysis, and applicable in situ, avoiding using specific materials or personnel to undergo the test, are highly desirable. In this regard, developing an electrochemical biosensor based on peptides derived from the angiotensin-converting enzyme receptor 2 (ACE2) is a possible answer. To this end, an impedimetric detector was developed based on a graphite electrode surface modified with an ACE2 peptide-mimic. This sensor enables accurate quantification of recombinant 2019-nCoV spike RBD protein (used as a model analyte) within a linear detection range of 0.167-0.994 ng mL-1, providing a reliable method for detecting SARS-CoV-2. The observed sensitivity was further demonstrated by molecular dynamics that established the high affinity and specificity of the peptide to the protein. Unlike other impedimetric sensors, the herein presented system can detect impedance in a single frequency, allowing a measure as fast as 3 min to complete the analysis and achieving a detection limit of 45.08 pg mL-1. Thus, the proposed peptide-based electrochemical biosensor offers fast results with adequate sensitivity, opening a path to new developments concerning other viruses of interest.
Keywords: ACE2 peptide-mimic; biosensors; graphite surface; impedimetric detection; spike protein detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of Ni-ZnO-ACE-2 peptide hybrids as electrochemical devices for SARS-CoV-2 spike protein detection.Bioelectrochemistry. 2025 Jun;163:108899. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2025.108899. Epub 2025 Jan 4. Bioelectrochemistry. 2025. PMID: 39793516
-
Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein using a magnetic-assisted electrochemical biosensor based on functionalized CoFe2O4 magnetic nanomaterials.Talanta. 2024 Jul 1;274:125986. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.125986. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Talanta. 2024. PMID: 38537348
-
Peptide-based simple detection of SARS-CoV-2 with electrochemical readout.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 May 1;1205:339739. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.339739. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35414399 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of biosensors for detection of SARS-CoV-2 variants based on ACE2.Talanta. 2023 Jan 1;251:123813. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123813. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 35952504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 detection: Voltametric or impedimetric transduction?Bioelectrochemistry. 2022 Oct;147:108190. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2022.108190. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Bioelectrochemistry. 2022. PMID: 35738049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

