Development of a Novel Colorimetric pH Biosensor Based on A-Motif Structures for Rapid Food Freshness Monitoring and Spoilage Detection
- PMID: 39727870
- PMCID: PMC11674138
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14120605
Development of a Novel Colorimetric pH Biosensor Based on A-Motif Structures for Rapid Food Freshness Monitoring and Spoilage Detection
Abstract
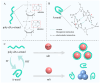
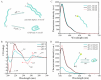
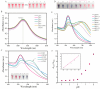
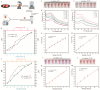
Accurate methods for assessing food freshness through colorimetric pH response play a critical role in determining food spoilage and ensuring food quality standards. This study introduces a novel unlabeled DNA sequence, poly-dA20, designed to exploit the colorimetric properties of both the single strand and the fold-back A-motif structure in conjunction with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) under varying pH conditions. When exposed to storage temperatures of 4 °C and 25 °C, the color variations in the AuNP solution, influenced by pH level changes in mutton and sea bass samples' different storage periods, are easily discernible to the naked eye within a minute. The ratio of UV absorption values at 527 nm and 700 nm (A527/A700) demonstrates a strong linear correlation with both the storage duration and pH of the food samples. Furthermore, a comprehensive analysis combining the total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) value with the A527/A700 ratio is employed for precise assessment of food freshness. The innovative pH-responsive sensing strategy not only provides a new approach for on-site food freshness and spoilage detection systems but also serves as a valuable tool for pH-related biological detection in clinical diagnostic applications.
Keywords: A-motif; colorimetric detection strategy; food safety; pH-responsive DNA nanostructures; smart biosensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Koutsoumanis K., Tsaloumi S., Aspridou Z., Tassou C., Gougouli M. Application of Quantitative Microbiological Risk Assessment (QMRA) to food spoilage: Principles and methodology. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021;114:189–197. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.011. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

