Antimicrobial Responses to Bacterial Metabolic Activity and Biofilm Formation Studied Using Microbial Fuel Cell-Based Biosensors
- PMID: 39727871
- PMCID: PMC11674809
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14120606
Antimicrobial Responses to Bacterial Metabolic Activity and Biofilm Formation Studied Using Microbial Fuel Cell-Based Biosensors
Abstract
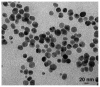
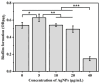
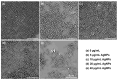
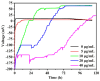
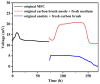
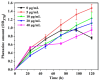
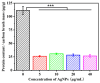
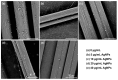
Simultaneous monitoring of antimicrobial responses to bacterial metabolic activity and biofilm formation is critical for efficient screening of new anti-biofilm drugs. A microbial fuel cell-based biosensor using Pseudomonas aeruginosa as an electricigen was constructed. The effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on the cellular metabolic activity and biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa in the biosensors were investigated and compared with the traditional biofilm detection method. The crystal violet staining results showed that the concentration of AgNPs being increased to 20 and 40 μg/mL had a slight and obvious inhibitory effect on biofilm formation, respectively. In comparison, the detection sensitivity of the biosensor was much higher. When the concentration of AgNPs was 5 μg/mL, the output voltage of the biosensor was suppressed, and the inhibition gradually increased with the AgNPs dose. AgNPs inhibited the activity of planktonic cells in the anolyte and the formation of biofilm on the anode surface, and it had a dose-dependent effect on the secretion of phenazine in the anolyte. The biosensor could monitor the impacts of AgNPs not only on biofilm formation but also on cell activity and metabolic activity. It provides a new and sensitive method for the screening of anti-biofilm drugs.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; biosensor; microbial fuel cell; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

