Electrochemical Magnetic Immunoassay for the Determination of the Fish Allergen β-Parvalbumin
- PMID: 39727904
- PMCID: PMC11674945
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14120639
Electrochemical Magnetic Immunoassay for the Determination of the Fish Allergen β-Parvalbumin
Abstract
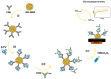
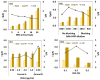
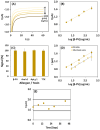
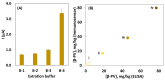
β-parvalbumin (β-PV) is the primary fish allergen responsible for most allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to fish. To ensure food safety, a sandwich-based magnetic immunoassay was developed using maleimide-functionalized magnetic beads (NH-MBs). Specific anti-β-PV antibodies were immobilized on these MBs, and a screen-printed carbon electrode was employed as the electrochemical transducer. A linear concentration range from 10 to 1000 ng/mL, a limit of detection of 1.8 ng/mL, and a limit of quantification of 7.1 ng/mL were achieved. Nineteen commercial food samples were analyzed to assess the potential of the sensor for routine use in food quality control. Important factors such as protein source and food processing (e.g., boiling, grilling, and frying) and preservation (e.g., in oil, and vacuum) were evaluated. The validated results confer the usefulness of the assay for food quality control.
Keywords: chronoamperometry; electrochemical biosensor; fish allergen; food safety; immunomagnetic assay; maleimide-modified magnetic-beads; seafood; β-parvalbumin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Seafood product safety: A hybrid graphene/gold-based electrochemical immunosensor for fish allergen analysis.Food Chem. 2024 Jul 15;446:138889. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138889. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38452504
-
Detection of Ara h 1 (a major peanut allergen) in food using an electrochemical gold nanoparticle-coated screen-printed immunosensor.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 Feb 15;64:19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.08.026. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 25173734
-
Fluorescent magnetic bead-based mast cell biosensor for electrochemical detection of allergens in foodstuffs.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 Aug 15;70:482-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.03.058. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 25889258
-
Electrochemical Affinity Biosensors Based on Disposable Screen-Printed Electrodes for Detection of Food Allergens.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Nov 5;16(11):1863. doi: 10.3390/s16111863. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27827963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Fish Parvalbumins through Allergen Names and Gene Identities.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;15(10):1337. doi: 10.3390/genes15101337. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457461 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saidi A., Cavallo C., Del Giudice T., Vecchio R., Cicia G. Consumer preferences for finfish: A systematic literature review. Food Qual. Prefer. 2023;105:104786. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2022.104786. - DOI
-
- Sun Y., Luo Y., Chen J., Liu X., Gao J., Xie Y., Chen H. Fish Allergy: A Review of Clinical Characteristics, Mechanism, Allergens, Epitopes, and Cross-Reactivity. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2024;4:304–315. doi: 10.1021/acsfoodscitech.3c00572. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UIDB/50006/2020, DOI: 10.54499/UIDB/50006/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- LA/P/0008/2020, DOI: 10.54499/LA/P/0008/2020, UIDP/50006/2020, DOI: 10.54499/UIDP/50006/2020, PTDC/QUI-QAN/30735/2017, DOI: 10.54499/PTDC/QUI-QAN/30735/2017, 2020.06987.BD, DOI: 10.54499/0000-0001-5968-0969, 2022.00490.CEECIND/CP1724/CT0007, DOI: 10.54499/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

