Suprathel Versus Hypafix in the Management of Split-Thickness Donor Site Wounds in the Elderly: A Randomised Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39727907
- PMCID: PMC11727311
- DOI: 10.3390/ebj5040031
Suprathel Versus Hypafix in the Management of Split-Thickness Donor Site Wounds in the Elderly: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
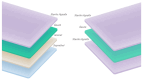
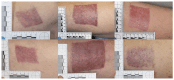
(1) Background: Effective wound management aims for expedited healing, improved functional and scar outcomes, and reduced complications including infection. Delayed wound healing remains a prevalent problem in the elderly. Suprathel is a synthetic absorbable skin substitute and an attractive option in partial thickness wounds. The objective of this randomised controlled study was to assess the effect of skin substitute dressings on elderly split-skin graft (STSG) donor sites, evaluating time to heal, pain, itch and scar outcome. (2) Methods: 40 patients over 65 undergoing split-thickness skin grafting for non-melanoma skin cancer excision were randomised to STSG donor site dressings with either Suprathel or Hypafix. Patients were followed up weekly until healed and at 13 weeks post-procedure. (3) Results: There was no significant difference in time to healing, pain, itch, or scar outcome at 13 weeks between the two groups. The mean time to healing was 31.7 days for the skin substitute group and 27.3 days for the adhesive tape control group (p = 0.182). (4) Conclusions: Both dressings are appropriate for STSG donor sites. Hypafix remains a cost-effective dressing of choice for donor sites. Benefits demonstrated in other studies using skin substitutes have not translated into the elderly population. There remains scope in developing dressings that reduce elderly donor site morbidity.
Keywords: Suprathel; epidermal skin substitute; split-thickness skin graft; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. PolyMedics Innovations GmbH had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Ashcroft G.S., Horan M.A., Herrick S.E., Tarnuzzer R.W., Schultz G.S., Ferguson M.W. Age-related differences in the temporal and spatial regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in normal skin and acute cutaneous wounds of healthy humans. Cell Tissue Res. 1997;290:581–591. doi: 10.1007/s004410050963. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van de Kar A.L., Corion L.U.M., Smeulders M.J.C., Draaijers L.J., van der Horst C.M.A.M., van Zuijlen P.P.M. Reliable and feasible evaluation of linear scars by the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005;116:514–522. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000172982.43599.d6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
