Clinical Trial of Autologous Dendritic Cell Administration Effect on Water Molecule Diffusion and Anti-Inflammatory Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 39727950
- PMCID: PMC11727518
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46120822
Clinical Trial of Autologous Dendritic Cell Administration Effect on Water Molecule Diffusion and Anti-Inflammatory Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
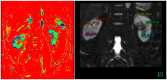
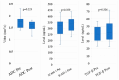
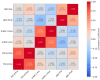
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) significantly increases mortality, with patients facing a fourfold risk of death within ten years. Chronic inflammation, marked by transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) activity, contributes to kidney damage and fibrosis. This study investigates the effect of autologous dendritic cells on inflammation and kidney function, focusing on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), TGF-β, and ICAM-1 levels. This quasi-experimental clinical trial involved 22 DKD patients at Gatot Soebroto Army Hospital. Patients received autologous dendritic cell injections. Baseline and post-intervention magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans measured ADC values, and ICAM-1 and TGF-β levels were analyzed. Post intervention, the median ADC decreased from 1.75 mm2/s to 1.64 mm2/s (p = 0.223). ICAM-1 levels increased significantly in females (p = 0.04) but not in males (p = 0.35). No significant changes were found in TGF-β levels (p = 0.506). ADC changes were statistically insignificant and did not correlate with CKD severity. ICAM-1 increases in females correlated with improved creatinine levels, suggesting kidney function improvement. Autologous dendritic cell therapy revealed potential gender-specific immune responses but showed limited overall biomarker improvements. Further studies are required to validate its therapeutic value.
Keywords: apparent diffusion coefficient; autologous dendritic cells; diabetic kidney disease; diffusion-weighted MRI; intracellular adhesion molecule-1; transforming growth factor-β.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- James S.L., Abate D., Abate K.H., Abay S.M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdela J., Abdelalim A., et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 Diseases and Injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pernefri 11th Report of Indonesian Renal Registry 2018. 2018. [(accessed on 15 May 2024)]. Available online: https://www.indonesianrenalregistry.org/
-
- Nurtandhee M. Estimasi Biaya Pelayanan Kesehatan sebagai Upaya Pencegahan Defisit Dana Jaminan Sosial untuk Penyakit Gagal Ginjal. J. Jaminan Kesehat. Nas. 2023;3:84–101. doi: 10.53756/jjkn.v3i2.104. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

