Genome-Wide Identification, Expression and Interaction Analysis of GLN Gene Family in Soybean
- PMID: 39727975
- PMCID: PMC11674948
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46120847
Genome-Wide Identification, Expression and Interaction Analysis of GLN Gene Family in Soybean
Abstract
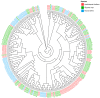
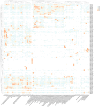
As a globally significant economic crop, the seed size of soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.) is jointly regulated by internal genetic factors and external environmental signals. This study discovered that the GLN family proteins in soybean are similar to the KIX-PPD-MYC transcriptional repressor complex in Arabidopsis, potentially influencing seed size by regulating the expression of the downstream gene GIF1. Additionally, β-1,3-glucanase (βGlu) plays a crucial role in antifungal activity, cell composition, flower development, pollen development, abiotic resistance, seed germination, and maturation in soybean. Through a detailed analysis of the structure, chromosomal localization, phylogenetic relationships, and expression situations in different tissues at different stages of the soybean GLN gene family members, this research certifies a theoretical foundation for subsequent research on the biological functions of GLN genes in soybean. This research incorporated a comprehensive genomic identification and expression analysis of the GLN gene family in soybean. The results indicate that the 109 soybean GLN genes are unevenly distributed across soybean chromosomes and exhibit diverse expression patterns in different tissues, suggesting they may have distinct functions in soybean morphogenesis. GO enrichment analysis shows that the GLN gene family may participate in a variety of biological activities, cellular components, and molecular biological processes, particularly in catalytic activity, cellular components, and metabolic processes. These findings provide important information for comprehending the role of the GLN gene family in soybean and offer potential targets for molecular breeding of soybean.
Keywords: GLN gene family; expression pattern; seed size; soybean.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

