LncRNA Expression Profiles in C6 Ceramide Treatment Reveal lnc_025370 as a Promoter in Canine Mammary Carcinoma CHMp Cells Progression
- PMID: 39727977
- PMCID: PMC11674213
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46120849
LncRNA Expression Profiles in C6 Ceramide Treatment Reveal lnc_025370 as a Promoter in Canine Mammary Carcinoma CHMp Cells Progression
Abstract
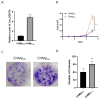
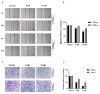
Canine mammary carcinomas (CMCs) represent the most prevalent form of cancer in female dogs, characterized by a high incidence and mortality rate. C6 ceramide is recognized for its multifaceted anti-cancer properties, yet its specific influence on CMCs remains to be elucidated. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), now recognized as functional "dark matter" in precision oncology, are particularly intriguing, with 44% of canine lncRNAs exhibiting tissue-specific expression. In this study, we performed a thorough analysis of lncRNA expression profiles to uncover the mechanisms behind C6 ceramide's anti-cancer activity in CHMp cells. Our findings reveal that C6 ceramide notably inhibits the proliferation of CHMp cells. RNA sequencing identified 4522 lncRNAs with expression changes following C6 ceramide treatment, of which 2936 were upregulated and 1586 were downregulated. Further investigation into Lnc_025370 showed that it is predominantly nuclear-localized and is significantly downregulated by C6 ceramide treatment. Functional studies discovered that overexpression of Lnc_025370 enhances the growth and metastatic capabilities of CHMp cells, which is associated with an increase in NRG1, and concurrently diminishes the anti-cancer effectiveness of C6 ceramide in vitro. Mouse xenograft models also showed that Lnc_025370 overexpression promotes tumor growth and Ki67 expression. Together, our results suggest that Lnc_025370 acts as a pivotal target mediator of C6 ceramide's anti-cancer effects, facilitating the malignant progression of CHMp cells.
Keywords: C6 ceramide; Lnc_025370; NRG1; canine mammary carcinomas; expression profiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

