Immunolocalization of Na(+)-Dependent Glucose Co-Transporters in Chicken Kidneys in Norm and During T-2 Mycotoxicosis (Primary Study)
- PMID: 39727982
- PMCID: PMC11674384
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46120854
Immunolocalization of Na(+)-Dependent Glucose Co-Transporters in Chicken Kidneys in Norm and During T-2 Mycotoxicosis (Primary Study)
Abstract
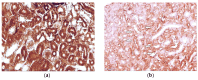
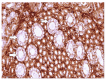
The kidney plays an essential role in the proper homeostasis of glucose. In the kidney, glucose transport is carried out across cell membranes by two families of glucose transporters-facilitated diffusion glucose transporters (GLUTs) and Na(+)-dependent glucose co-transporters (SGLT family). Among the transporters, sodium-dependent glucose co-transporters play a major role in the kidney's ability to reabsorb glucose. Although the localization of glucose transporters has been extensively studied in mammals, there are still knowledge gaps regarding the localization of SGLTs in birds. The aim of this research was to conduct a comparative study of the immunolocalization of the sodium-dependent glucose co-transporters SGLT1 and SGLT2 in the kidneys of healthy and T-2-mycotoxicated chickens. Immunohistochemical staining was carried out using the polyclonal primary antibodies SGLT1 and SGLT2 (Abcam, UK) in kidney tissue derived from seven healthy and seven T-2-mycotoxicated 7-day-old female layer-type Ross chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus). The sections were stained using an immunohistochemistry kit (Abcam, UK). In the kidneys of the healthy birds, strong staining of SGLT1 and SGLT2 was observed in the cytoplasm of the epithelial cells of the proximal straight and convoluted tubules. In the kidneys of the birds of the T-2 toxin group, weak expression of SGLT1 and SGLT2 with morphological changes occurred, indicating reduced glucose transport in the urinary system during T-2 mycotoxicosis.
Keywords: chicken; immunohistochemistry; mycotoxicosis; sodium-dependent glucose co-transporter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Immunolocalization of sodium-dependent glucose co-transporter 1 and sodium-dependent glucose co-transporter 2 in chicken's (Gallus gallus domesticus) kidneys.Pol J Vet Sci. 2024 Sep;27(3):323-328. doi: 10.24425/pjvs.2024.149363. Pol J Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39736118
-
Immunohistochemical Study of Glucose Transporter GLUT-5 in Duodenal Epithelium in Norm and in T-2 Mycotoxicosis.Foods. 2020 Jun 29;9(7):849. doi: 10.3390/foods9070849. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32610537 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the physiological roles of SGLTs and GLUTs using positron emission tomography in mice.J Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;594(15):4425-38. doi: 10.1113/JP271904. Epub 2016 May 10. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27018980 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Products as Lead Compounds for Sodium Glucose Cotransporter (SGLT) Inhibitors.Planta Med. 2017 Aug;83(12-13):985-993. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-106050. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Planta Med. 2017. PMID: 28395363 Review.
-
What does sodium-glucose co-transporter 1 inhibition add: Prospects for dual inhibition.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Apr;21 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):43-52. doi: 10.1111/dom.13630. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019. PMID: 31081587 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hruby V.J. In: Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. Bittar E., Bittar N., editors. Volume 10. JAI Press Inc.; Greenwhich, CT, USA: 1997. pp. 387–401.
-
- Mota M., Mota E., Dinu I.R. In: Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Croniger C., editor. IntechOpen; Rijeka, Crotaia: 2015. pp. 13–17. Chapter 1.
-
- König H.E., Korbel R., Liebich H.G. Avian Anatomy Textbook and Colour Atlas. Volume 2. 5m Publishing; Sheffield, UK: 2016. pp. 131–133.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

