Towards Effective Treatment of Glioblastoma: The Role of Combination Therapies and the Potential of Phytotherapy and Micotherapy
- PMID: 39727987
- PMCID: PMC11674107
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46120859
Towards Effective Treatment of Glioblastoma: The Role of Combination Therapies and the Potential of Phytotherapy and Micotherapy
Abstract
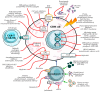
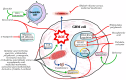
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is one of the most aggressive and difficult-to-treat brain tumors, with a poor prognosis due to its high resistance to conventional therapies. Current treatment options, including surgical resection, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, have limited effectiveness in improving long-term survival. Despite the emergence of new therapies, monotherapy approaches have not shown significant improvements, highlighting the need for innovative therapeutic strategies. Combination therapies appear to be the most promising solution, as they target multiple molecular pathways involved in GBM progression. One area of growing interest is the incorporation of phytotherapy and micotherapy as complementary treatments, which offer potential benefits due to their anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. This review examines the current challenges in GBM treatment, discusses the potential of combination therapies, and highlights the promising role of phytotherapy and micotherapy as integrative therapeutic options for GBM management.
Keywords: combined therapy; conventional therapy; glioblastoma; innovative therapy; natural adjuvant; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Wesseling P., Brat D.J., Cree I.A., Figarella-Branger D., Hawkins C., Ng H.K., Pfister S.M., Reifenberger G., et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-oncology. 2021;23:1231–1251. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

