Construction of an Integration Vector with a Chimeric Signal Peptide for the Expression of Monoclonal Antibodies in Mammalian Cells
- PMID: 39727996
- PMCID: PMC11674113
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46120868
Construction of an Integration Vector with a Chimeric Signal Peptide for the Expression of Monoclonal Antibodies in Mammalian Cells
Abstract
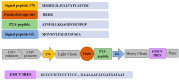
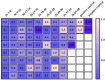
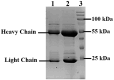
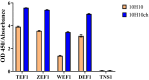
Antibodies are complex protein structures, and producing them using eukaryotic expression systems presents significant challenges. One frequently overlooked aspect of expression vectors is the nucleotide sequence encoding the signal peptide, which plays a pivotal role in facilitating the secretion of recombinant proteins. This study presents the development of an integrative vector, pVEAL3, for expressing full-length recombinant monoclonal antibodies in mammalian cells. The vector features a distinctive nucleotide sequence that encodes an artificial chimeric signal peptide with the following amino acid sequence: MMRTLILAVLLVYFCATVHC. Additionally, the vector incorporates several regulatory elements to enhance antibody expression, including the Gaussia luciferase signal sequence, internal ribosome entry site (IRES), P2A peptide, and a furin cleavage site. These elements coordinate to regulate the synthesis levels of the antibody chains. The analysis of clones obtained via transfection with the developed vector showed that over 95% of them secreted antibodies at levels significantly higher than those of the control. The immunochemical analysis of the chimeric antibody produced by the CHO-K1-10H10ch cell line confirmed the preservation of its functional activity.
Keywords: CHO-K1; artificial signal sequence; integrative vectors; recombinant antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of Signal Peptides on Furin-2A Mediated Monoclonal Antibody Secretion in CHO Cells.Biotechnol J. 2017 Sep;12(9). doi: 10.1002/biot.201700268. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 28727292
-
Comparison of internal ribosome entry site (IRES) and Furin-2A (F2A) for monoclonal antibody expression level and quality in CHO cells.PLoS One. 2013 May 21;8(5):e63247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063247. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23704898 Free PMC article.
-
Construction strategies for developing expression vectors for recombinant monoclonal antibody production in CHO cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Dec;45(6):2907-2912. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4351-0. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30191354
-
Cleavage efficient 2A peptides for high level monoclonal antibody expression in CHO cells.MAbs. 2015;7(2):403-12. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1008351. MAbs. 2015. PMID: 25621616 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of different vector designs for the mammalian expression of recombinant IgG antibodies.J Immunol Methods. 2007 Jan 10;318(1-2):113-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2006.10.010. Epub 2006 Nov 13. J Immunol Methods. 2007. PMID: 17161420
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

