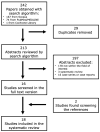
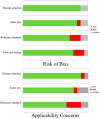
The Role of 11C-Methionine PET Imaging for the Evaluation of Lymphomas: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39728002
- PMCID: PMC11675220
- DOI: 10.3390/hematolrep16040072
The Role of 11C-Methionine PET Imaging for the Evaluation of Lymphomas: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: In the last years, different evidence has underlined a possible role for [11C]-methionine ([11C]MET) positron emission tomography (PET) imaging for the evaluation of lymphomas. The aim of this paper was, therefore, to review the available scientific literature focusing on this topic. Methods: A wide literature search of the PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus and Cochrane Library databases was conducted in order to find relevant published articles investigating the role of [11C]MET in the assessment of lymphomas. Results: Eighteen studies were included in the systematic review and the main fields of application of this imaging modality were the evaluation of disease, therapy response assessment, prognostic evaluation and differential diagnosis with other pathological conditions. Conclusion: Even with heterogeneous evidence, a possible role for [11C]MET PET imaging in the assessment of lymphomas affecting both the whole body and the central nervous system was underlined. When compared to [18F]fluorodesoxyglucose ([18F]FDG) imaging, in general, similar results have been reported between the two modalities in these settings.
Keywords: 11C-methionine; DLBCL; PET; PET/CT; central nervous system; lymphoma; positron emission tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Buck A.K., Bommer M., Juweid M.E., Glatting G., Stilgenbauer S., Mottaghy F.M., Schulz M., Kull T., Bunjes D., Möller P., et al. First demonstration of leukemia imaging with the proliferation marker 18F-fluorodeoxythymidine. J. Nucl. Med. 2008;49:1756–1762. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.055335. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dondi F., Pasinetti N., Gatta R., Albano D., Giubbini R., Bertagna F. Comparison between Two Different Scanners for the Evaluation of the Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT Semiquantitative Parameters and Radiomics Features in the Prediction of Final Diagnosis of Thyroid Incidentalomas. J. Clin. Med. 2022;11:615. doi: 10.3390/jcm11030615. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous