Discovery and Characterization of an Atypical Crustin Antimicrobial Peptide from Pollicipes pollicipes
- PMID: 39728101
- PMCID: PMC11678330
- DOI: 10.3390/md22120526
Discovery and Characterization of an Atypical Crustin Antimicrobial Peptide from Pollicipes pollicipes
Abstract
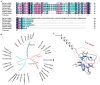
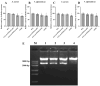
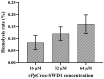
Crustins are a family of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) that play a pivotal role in the innate immune system of crustaceans. The discovery of novel AMPs from natural sources is crucial for expanding our current database of these peptides. Here, we identified and characterized a novel member of the crustin family, named PpCrus-SWD1, derived from Pollicipes pollicipes. PpCrus-SWD1 consists of 138 amino acids and contains eight cysteine residues that form a conserved 'four-disulfide core' structure. Our recombinant PpCrus-SWD1 (rPpCrus-SWD1) exhibited potent inhibitory activity against three Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus sp. T2, and Streptococcus agalactiae) and six Gram-negative bacteria (Aeromonas hydrophila, Escherichia coli, Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio parahemolyticus, and Acinetobacter sp. L3), with minimum inhibitory concentrations ranging from 16 to 64 μM. Furthermore, rPpCrus-SWD1 demonstrated binding affinity towards both bacteria and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), and damaged bacterial barrier. Additionally, it effectively inhibited alkaline protease activity in S. aureus and V. alginolyticus strains. These findings highlight the potential utility of this newly discovered crustin as an effective alternative to antibiotics.
Keywords: Pollicipes pollicipes; antibacterial mechanism; antibiotic; antimicrobial peptides; crustin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Heterologous Expression and Antimicrobial Mechanism of a Cysteine-Rich Peptide from Barnacle Pollicipes pollicipes.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 13;13(6):1381. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061381. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572268 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Characterization of a New Crustin Antimicrobial Peptide from Amphibalanus amphitrite.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 14;14(2):413. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020413. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214145 Free PMC article.
-
A new crustin homologue (SpCrus6) involved in the antimicrobial and antiviral innate immunity in mud crab, Scylla paramamosain.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Jan;84:733-743. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.10.072. Epub 2018 Oct 28. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30381264
-
Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Bacteria: Classification, Sources, and Mechanism of Action against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 8;25(19):10788. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910788. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update of peptides with antibacterial activity.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(36):6188-98. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22978329 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterologous Expression and Antimicrobial Mechanism of a Cysteine-Rich Peptide from Barnacle Pollicipes pollicipes.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 13;13(6):1381. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061381. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572268 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Expression and Antimicrobial Targets of a Novel Glycine-Rich Antimicrobial Peptide from Artemia franciscana.Mar Drugs. 2025 Aug 17;23(8):330. doi: 10.3390/md23080330. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40863648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aisenbrey C., Marquette A., Bechinger B. Antimicrobial Peptides. Springer; Singapore: 2019. The Mechanisms of Action of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides Refined by Novel Concepts from Biophysical Investigations; pp. 33–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

