Tetrodotoxin: The State-of-the-Art Progress in Characterization, Detection, Biosynthesis, and Transport Enrichment
- PMID: 39728106
- PMCID: PMC11676112
- DOI: 10.3390/md22120531
Tetrodotoxin: The State-of-the-Art Progress in Characterization, Detection, Biosynthesis, and Transport Enrichment
Abstract
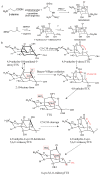
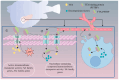
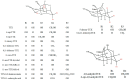
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a neurotoxin that binds to sodium channels and blocks sodium conduction. Importantly, TTX has been increasingly detected in edible aquatic organisms. Because of this and the lack of specific antidotes, TTX poisoning is now a major threat to public health. However, it is of note that ultra-low dose TTX is an excellent analgesic with great medicinal value. These contradictory effects highlight the need for further research to elucidate the impacts and functional mechanisms of TTX. This review summarizes the latest research progress in relation to TTX sources, analogs, mechanisms of action, detection methods, poisoning symptoms, therapeutic options, biosynthesis pathways, and mechanisms of transport and accumulation in pufferfish. This review also provides a theoretical basis for reducing the poisoning risks associated with TTX and for establishing an effective system for its use and management to ensure the safety of fisheries and human health.
Keywords: TTX biosynthesis; TTX transporter accumulation; puffer fish; tetrodotoxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Suehiro M. Historical review on chemical and medical studies of globefish toxin before World War II. Yakushigaku Zasshi. 1994;29:428–434. - PubMed
-
- Kotipoyina H.R., Kong E.L., Chen R.J., Warrington S.J. Tetrodotoxin Toxicity. StatPearls Publishing LLC; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. - PubMed
-
- Asakawa M., Matsumoto T., Umezaki K., Kaneko K., Yu X., Gomez-Delan G., Tomano S., Noguchi T., Ohtsuka S. Toxicity and toxin composition of the greater blue-ringed octopus Hapalochlaena lunulata from ishigaki island, okinawa prefecture, Japan. Toxins. 2019;11:245. doi: 10.3390/toxins11050245. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

