Lithium Coupled with C6-Carboxyl Improves the Efficacy of Oligoguluronate in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in C57BL/6J Mice
- PMID: 39728147
- PMCID: PMC11678007
- DOI: 10.3390/md22120573
Lithium Coupled with C6-Carboxyl Improves the Efficacy of Oligoguluronate in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
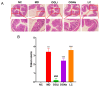
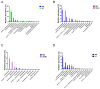
Oligoguluronate lithium (OGLi) was prepared for the purpose of enhancing the anti-ulcerative colitis (UC) activities of OG, in which lithium (Li+) is coupled with the C6-carboxyl of G residue. The therapeutic effects of OGLi on dextran sulfate (DSS)-induced UC mice were investigated, and oligoguluronate sodium (OGNa) and lithium carbonate (LC) were used as contrasts. The effects of OGLi, OGNa and LC on the treatment of UC mice were studied by monitoring body weight change and evaluating colon length, the disease activity index (DAI), histopathological examination and gut microbiota regulation. The results showed that compared with OGNa and LC, OGLi significantly reduced the clinical symptoms and histopathological changes associated with UC in the acute model. It was worth noting that OGLi significantly changed the gut microbiota characteristics of the DSS-treated mice and corrected the typical dysbacteriosis of DSS-induced UC. This intervention resulted in increasing the abundance of norank_f_Muribaculaceae and Ileibacterium spp. while reducing the levels of Escherichia-Shigella spp. and Romboutsia spp. The OGLi could significantly increase the diversity of intestinal microorganisms in the short term. All of these discoveries demonstrate that lithium collaboratively enhances the anti-UC efficacy of OG, which will help to create OG-based drugs for the treatment of UC.
Keywords: collaborative efficacy enhancement; gut microbiota; lithium; oligoguluronate; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mizuno S., Ono K., Mikami Y., Naganuma M., Fukuda T., Minami K., Masaoka T., Terada S., Yoshida T., Saigusa K., et al. 5-Aminosalicylic Acid Intolerance Is Associated with a Risk of Adverse Clinical Outcomes and Dysbiosis in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Intest. Res. 2020;18:69–78. doi: 10.5217/ir.2019.00084. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

